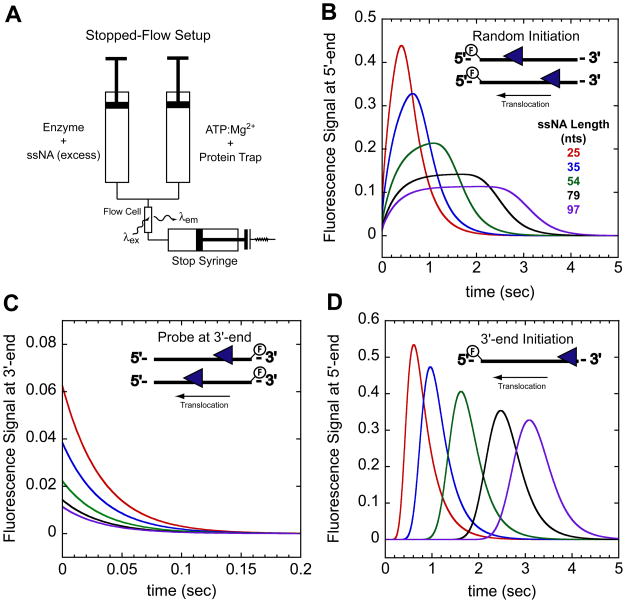
Figure 1.
Stopped-flow experimental setup and expected time courses for monitoring directionally biased translocation. (A)- Schematic of stopped-flow experiment. In one syringe enzyme is pre-incubated with excess ssNA labeled at either the 5′ or 3′end with a fluorophore. The enzyme:ssNA complex is rapidly mixed with ATP, Mg2+, and a protein trap to initiate translocation. Detection of changes in the fluorophore fluorescence intensity as the translocase nears the fluorophore indirectly monitors translocation. (B)- Example time courses monitoring arrival of a 3′ to 5′ translocase at the 5′-end of the ssNA when the translocase is initially bound to random sites along the ssNA. (C)- Example time courses monitoring the translocase leaving the 3′-end of the ssNA. In this experiment the ssNA is labeled at the 3′-end. Combing the experiments in (B) and (C) one can directly assess the directionality of translocation. (D)- Example time courses monitoring arrival of 3′ to 5′ translocase at the 5′-end of the ssNA when the translocase is initially bound at the 3′-end. The time courses were simulated with the following parameters described in the text mkt = 30 nts/sec, kd = 0 sec−1, kend = 3 sec−1, and m = 1 nt/step.