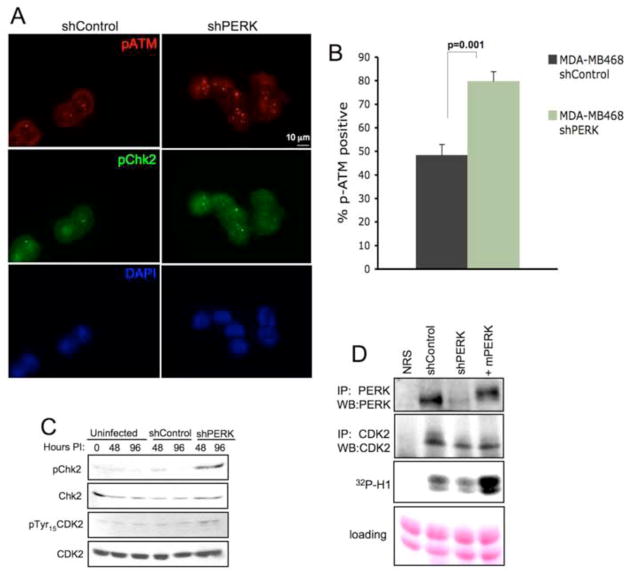
Figure 3. PERK knockdown triggers DNA damage response signaling pathway.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining for DNA damage-induced foci containing phospho-ATM and phospho-Chk2 following acute PERK knockdown (72 h after infection) in MDA-MB468 cells. (B) Quantification of phospho-ATM positive cells (>3 foci) is shown; error bars indicate S.D. from 3 slides, 5 fields were counted per slide. p-value was determined by Student t-test. (C) Western analysis of DNA damage response-associated markers following PERK knockdown. (D) IP/kinase assays assessing CDK2-dependent phosphorylation of histone H1 (bottom panel). CDK2 complexes were immunoprecipitated from MDA-MB 468 cells treated as indicated. PERK levels were assessed by IP/immunoblot and CDK2 recovery in precipitates was assessed by CDK2 immunoblot (middle panel).