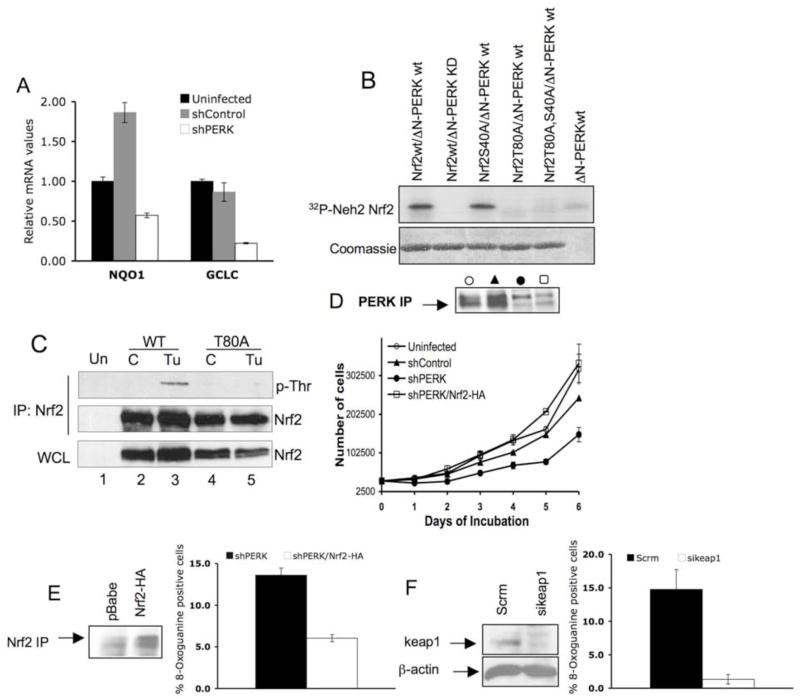
Figure 7. Reduced activity of Nrf2 causes increased oxidative stress in PERK knockdown cells.
(A) Quantitative real time PCR analysis of Nrf2 target genes NQO1 and GCLC in the indicated cell lines asynchronously proliferating under standard conditions. (B) Purified recombinant Nrf2-Neh2 domain of WT, T80A, S40A or T80A/S40A, was incubated with purified recombinant ΔN-PERK in the in vitro kinase assay. Phosphorylated Nrf2-Neh2 was detected by autoradiography (upper panel). (C) 293T cells were transfected with WT Nrf2 or Nrf2-T80A. 24 hours after transfection, cells were left untreated (C) or treated with tunicamycin (Tu) for 2 hours followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-Nrf2 antibody. Threonine phosphorylation was detected using a phospho-Thr reactive antibody. Nrf2 in the IP and the whole cell lysate (WCL) was detected with Nrf2 specific antibody. (D) Proliferation of the indicated cell lines was assessed by a 6-day growth curve under standard tissue culture conditions as described in materials and methods. PERK levels were detected by IP/Western blot analysis. (E) Oxidized guanine in damaged DNA was detected by a FITC-conjugated 8-OxoG binding peptide in PERK knockdown cells infected with pBabe control vector (shPERK) or Nrf2-HA (shPERK Nrf2-HA). Quantification of 8-OxoG positive cells is provided. Error bars represent S.D. from 3 experiments. (F) 8-OxoG was detected in PERK knockdown cells transfected with scramble siRNA (Scrm), or keap1 siRNA (sikeap1). Error bars in graphs represent S.D. from 3 experiments. Western blot panels demonstrate levels of Nrf2-HA and Keap1 in PERK knockdown cells.