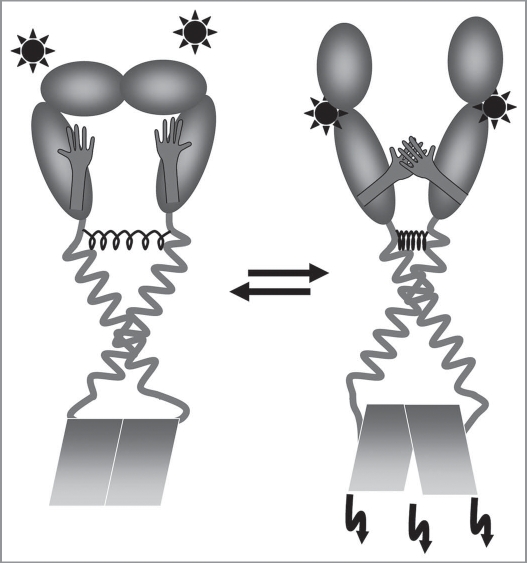
Figure 5.
A model of ErbB TM signaling. The preformed ErbB dimer is stabilized in the TM region by the C-terminal GxxxG-like motif. The energetically preferred TM structure stabilized by the N-terminal motif is hindered because of a steric barrier defined by the soluble extracellular domain. Ligand binding induces structural rearrangements in the ligand binding domain and allows the “strained spring” to relax, and the TM structure switches into the structure stabilized by the N-terminal GxxxG-like motif of the TMD as well as by interactions of the dimerization arms. This structural rearrangement places the two intracellular kinase domains into a different position resulting in kinase activation and in downstream signaling.