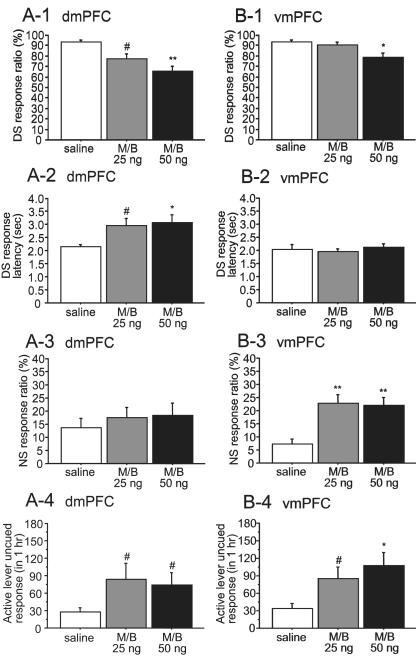
Fig. 6.
Distinct effects of dmPFC and vmPFC inactivation on DS behaviors. DS responding was impaired by dmPFC inactivation using 25 and 50 ng M/B (A-1), whereas only the 50 ng M/B dose injected into the vmPFC reduced the DS response ratio (B-1). M/B injection into the dmPFC increased DS response latency (A-2), whereas vmPFC inactivation had no effect on the latency (B-2). On the other hand, inactivation of the vmPFC but not the dmPFC induced a significant increase in the NS response ratio (A-3, B-3). Both dmPFC and vmPFC inactivation augmented uncued responses on the active lever (A-4, B-4). #P < 0.05, *P < 0.01 and **P < 0.001 compared with saline.