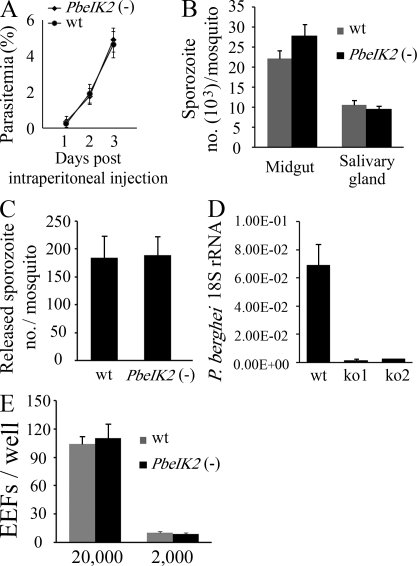
Figure 2.
Phenotype of PbeIK2 (-) sporozoites. (A) PbeIK2 (-) parasites develop normally in asexual blood stages. Swiss Webster mice (5 per group) were injected intraperitoneally with 200 µl of blood infected with PbeIK2 (-) or wild-type parasites (1% parasitemia). The parasitemia of the recipient mice was checked in Giemsa-stained blood smears. (B) PbeIK2 (-) and wild-type parasites produce the same number of midgut and salivary gland–associated sporozoites on day 14 and 20 after the first infectious blood meal, respectively. Sporozoite numbers were counted in three different mosquito cycles of the wild type and mutants. (C) PbeIK2 (-), and wild-type–infected mosquitoes release saliva containing the same number of sporozoites into the medium. Sporozoite numbers were counted in three independent experiments. (D) C57BL/6 mice (five mice per group) were intravenously injected with 1 × 104 wild type or either one of two clones of PbeIK2 (-) sporozoites (ko1 and ko2). Liver-stage parasite burden was measured by real-time RT-PCR, and shown are the means ± SD of two independent experiments. (E) In three independent experiments 2 × 104 or 2 × 103 wild-type and PbeIK2 (-) sporozoites were added to HepG2 cells. Infectivity of sporozoites to HepG2 cells were evaluated by counting EEF numbers 48 h after infection.