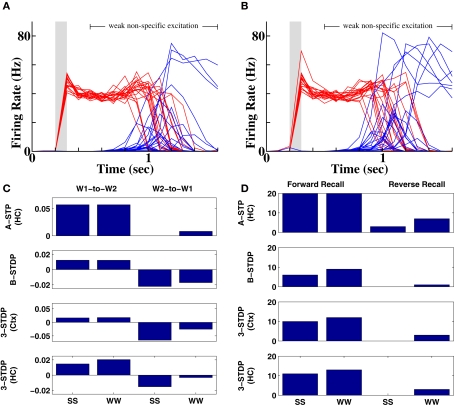
Figure 3.
Impossibility of reverse recall via connections between word populations. (A) 20 separate instantiations of the memory protocol, with activation of the second word produce chance recall of other words (3 out of 20 instantiations). In the unsuccessful examples, pools that did not receive prior input become activated by chance during recall. (B) Reverse recall is slightly greater than chance following weak inputs, where temporal overlap of activity is greater. (C) Comparison of changes in mean synaptic weight as a fraction of original synaptic strength between two word pools receiving successive input, as a function of input strength and plasticity mechanism. W1 = first word; W2 = second word. Prior stimuli were either both strong (SS) or both weak (WW). Top row = associative short-term plasticity; second row = basic STDP; third row = triplet-STDP with cortical parameters; bottom row = triplet-STDP with hippocampal parameters. (D) Number of correct recalls as a function of prior input strength and plasticity mechanism. Row and column labels as in (C).