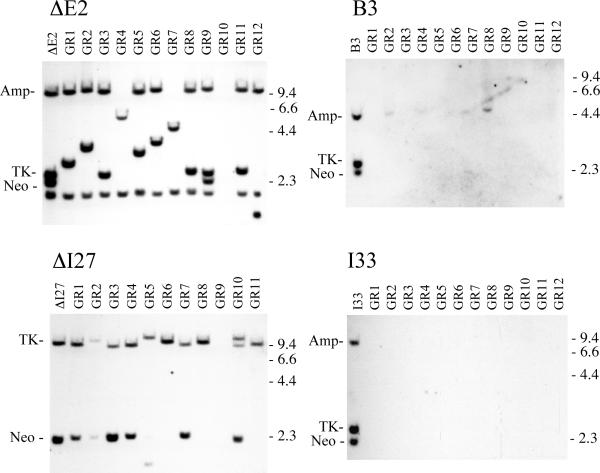
FIG. 4.
Southern blot analysis demonstrated that inactivation of the HSV-tk at telomeric sites most often results from large deletions involving loss of the integrated plasmid sequences. Genomic DNA from parental clones B3 and I33 with telomeric I-SceI sites, and ΔE2, ΔI27 with interstitial I-SceI sites, is compared with genomic DNA from 12 of their Ganr subclones infected with the pQCXIP-ISceI retrovirus (GR1 – GR12). The genomic DNA was digested with HindIII, and hybridization was performed using the pNTPΔ plasmid probe. pNTPΔ contains the amp, neo and HSV-tk genes, but lacks the telomeric repeat sequences. pNTPΔ also lacks the CMV promoter, which cross hybridizes with the CMV promoter in the pQCXIP retrovirus. The location of the bands containing the neo and HSV-tk genes, and the location of the lambda bacteriophage HindIII restriction fragments are shown.