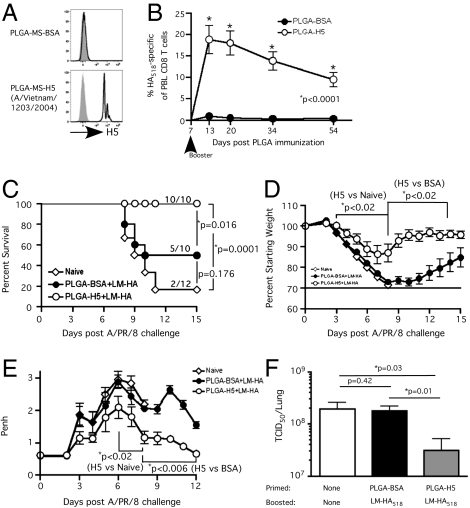
Fig. 4.
Protective heterosubtypic immunity against lethal influenza. (A) Detection of recombinant HA H5 (A/Vietnam/1203/2004) on PLGA microspheres by flow cytometry before mice were immunized. Shaded histograms indicate isotype controls. (B–F) Naïve BALB/c mice were immunized with ∼109 H5- or BSA-coated PLGA microspheres and received booster immunization with attLM-HA518 (Kd/IYSTVASSL) (∼107 cfu/mouse) on day 7. (B) Kinetics of HA518-specific CD8 T-cell response as detected by Kd/HA518 tetramer staining and expressed as mean frequency ± SEM (n = 5) of CD8 T cells (CD8+Thy1.2+) in PBL. (C–F) Naïve BALB/c mice and cross-prime-boost mice from B were challenged with a lethal dose (∼5 LD50) of influenza A/PR/8 (H1N1). (C) Kaplan–Meier survival curve; mortality is defined as > 30% loss of starting weight, mice are euthanized at this endpoint per IACUC guidelines. Numbers on the graph indicate number surviving mice/total number of mice. Log-rank test was used to generate P values for the survival curves. (D) Morbidity is measured by weight loss and expressed as percent of starting weight. (E) Airway resistance (Penh value) was measured before and at indicated time points after influenza A/PR/8/34 challenge. (F) Viral titer was determined from the lung 3 d after influenza challenge (n = 4). *Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired, two-tailed t test.