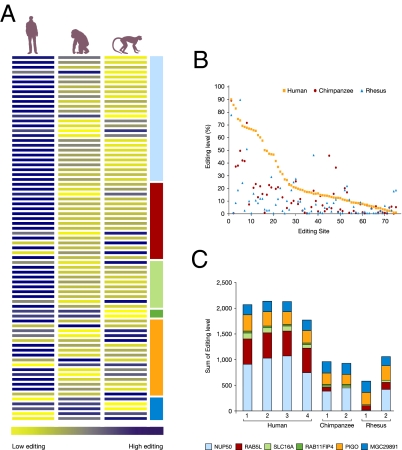
Fig. 1.
Higher editing level in human vs. nonhuman primates. (A) Editing levels of 75 sites in six transcripts originating from cerebellum tissues of four humans, two chimpanzees, and two rhesus monkeys were quantified after PCR amplification using the DSgene program. Average editing values were normalized (Z-score) and colored accordingly with blue-yellow gradient using the Spotfire program (Tibco). (B) Editing level per site for humans, chimpanzees, and rhesus monkeys. The human editing sites are ordered in decreasing editing levels, and the nonhuman primate editing sites are aligned, accordingly. (C) Editing levels in cerebellum tissues of eight individual primates: a total of the resulting editing level quantification in the six tested transcripts are plotted in four human, two chimpanzee, and two rhesus individuals where the bar size is proportional to the total of the editing levels in all tested sites.