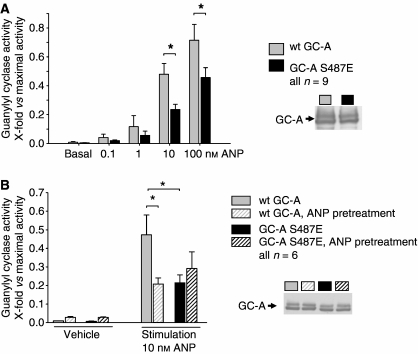
Fig. 6.
The impact of the phosphorylation of the GC-A receptor at Ser487 on the responsiveness and homologous desensitization of the receptor was characterized by site-directed mutagenesis followed by guanylyl cyclase activity assays. Crude membranes prepared from HEK293 cells expressing wild-type (wt) GC-A or GC-A S487E were incubated with vehicle, ANP or detergent (Triton X-100). cGMP production was measured by RIA [fmol cGMP·(μg protein)−1·min−1]. All values were calculated as X-fold of the maximal (Triton X-100-induced) activity (means ± SEM). The western blots shown in the insets demonstrate similar expression levels of wt and mutated GC-A (all 10 μg protein per lane). (A) ANP evoked concentration-dependent increases in GC-A activity. The GC-A S487E mutant showed significantly reduced responsiveness to ANP (n = 9 from three independent experiments). (B) HEK293 cells were pretreated with ANP (100 nm, 1 h) or vehicle before the preparation of cell membranes. ANP pretreatment decreased significantly the cGMP response of wt GC-A to subsequent stimulation with 10 nm ANP, indicating homologous desensitization. The GC-A S487E mutant showed a significantly diminished cGMP response to 10 nm ANP, which was not further inhibited by ANP pretreatment (n = 6 from three independent experiments).