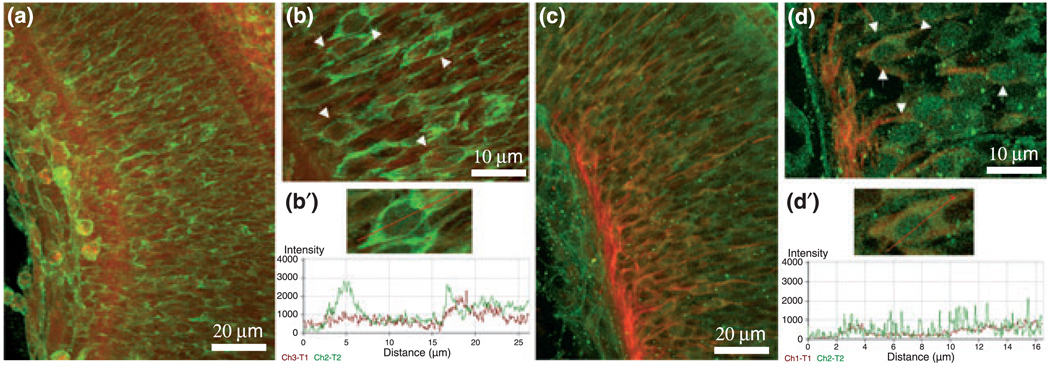
Fig. 6.
Immunostainings of osteopontin (OPN) and CD44 in the premature E15 RGC layer of 90 µm-thick vibratome sections. (a) Confocal image of 40× magnified RGC layer immunostained for OPN (green) and β-tubulin (red). (b) 100× magnification of the premature E15 ganglion cell layer (OPN, green; β-tubulin, red). Premature ganglion cells are marked by white arrows. (b′) ‘Profile’ from the laser scanning microscope (LSM) software along the red line shows OPN protein co-expressed with β-tubulin in one RGC. ‘Profile’ uses one image from a stack of images for analysis. (c) Confocal image of 40× magnified RGC layer immunostained for CD44 (green) and β-tubulin (red) in retinas of E15 embryos. (d) Higher magnification (100×) of the premature E15 ganglion cell layer (CD44, green; β-tubulin, red) marked by white arrows. (d′) ‘Profile’ from the LSM software package shows along the red line a clustered CD44 staining in areas of β-tubulin immunostaining in one RGC.