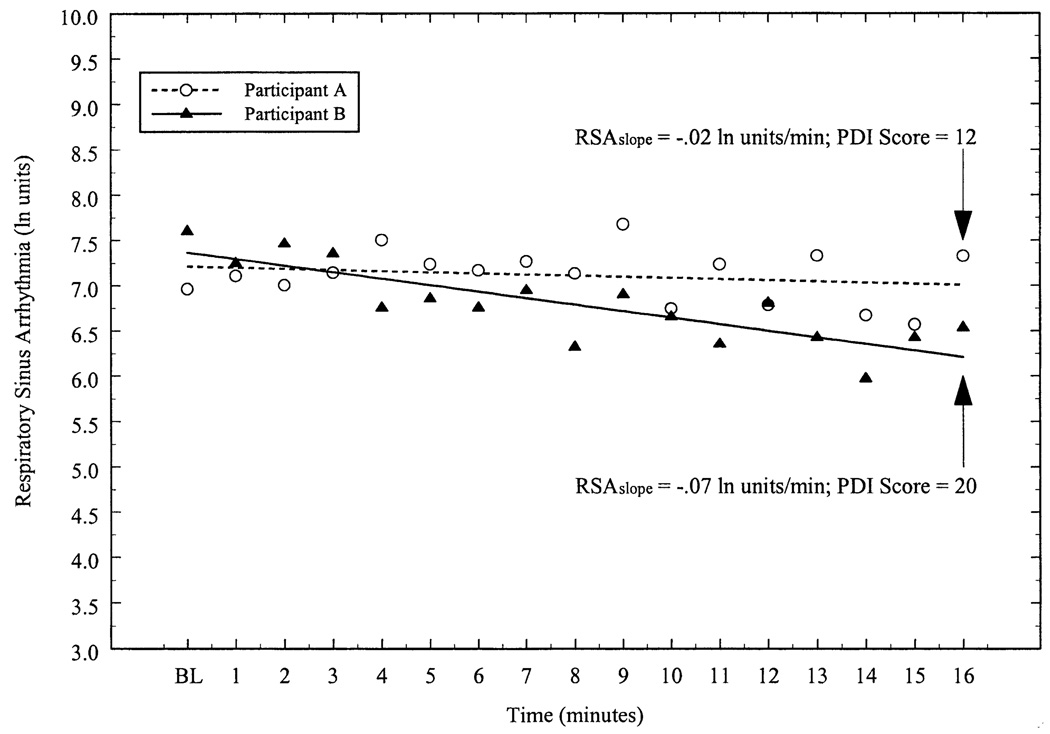
Figure 1.
Respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA) as a function of time for two participants. BL represents the average RSA from a 6-min baseline period; min 1–16 correspond to optokinetic drum rotation. Individual regression analyses were used to derive an unstandardized regression coefficient (RSAslope) that represented the change in RSA per minute. These regression coefficients were then correlated to motion sickness scores obtained from the Pensacola Diagnostic Index (PDI). The PDI scores for the participants shown here were reported at the 16th minute of drum rotation. In the present study, RSAslope values were inversely related to motion sickness scores, indicating that a greater degree of cardiac parasympathetic withdrawal over time was associated with increased motion sickness severity.