Figure.
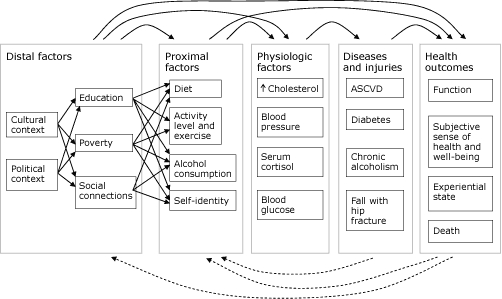
A causal web that illustrates various factors influencing health outcomes and interactions among them. Solid arrows represent potential causal relationships between factors, diseases, and outcomes. Dashed arrows represent potential feedback from outcomes and diseases on proximal and distal factors. Distal and proximal factors operate through both intermediate factors and directly on health outcomes. For example, a person's level of education can directly influence his or her subjective sense of health and level of social function and also influence intermediate factors, such as diet and exercise. Similarly, the understanding that death or loss of function may occur as the result of a person's lifestyle or social and economic factors, such as education and poverty, may influence those factors through either behavior change or changes in social or economic policy. Examples of factors, diseases, and injuries were chosen to provide a sense of the breadth of available factors. To improve readability, the relationships among proximal factors, physiologic factors, diseases and injuries, and health outcomes have been simplified. Adapted from references 4-6. Abbreviation: ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
