Fig. 2.
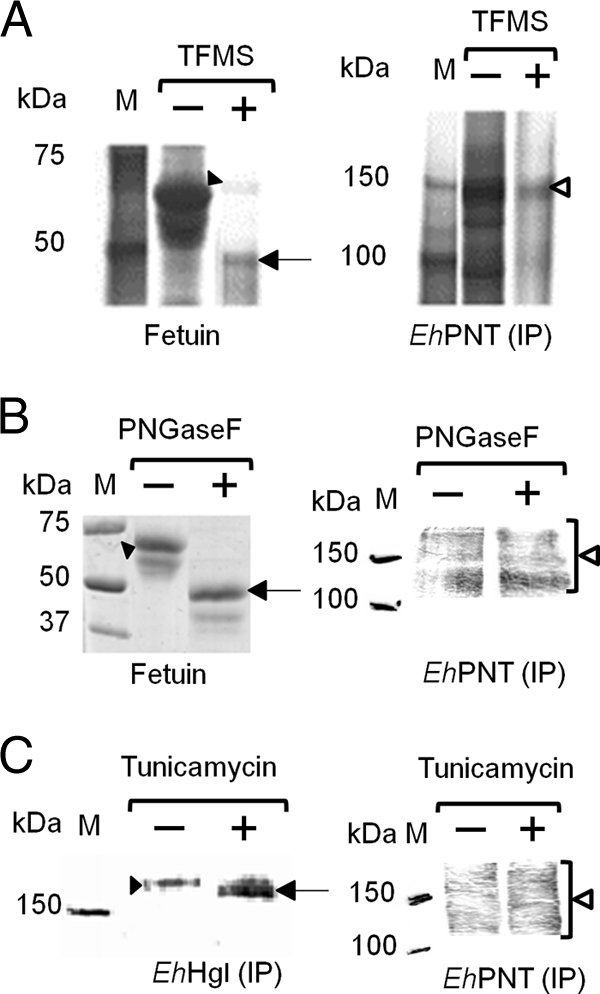
Deglycosylation of EhPNT. (A and B) Deglycosylation by TFMS or PNGase F. The lysates obtained from the transformant expressing EhPNT-HA were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-HA antibody, followed by TFMS or PNGase F treatment and immunoblot detection with anti-HA antibody (right). Fetuin was used as a control, and gels were stained with silver (A) or Coomassie brilliant blue (B) (left). Filled arrowheads indicate untreated fetuin. Arrows indicate fetuin deglycosylated by TFMS (A) or PNGase F (B). Open arrowheads indicate EhPNT. (C) Deglycosylation by tunicamycin. Lysates from the transformant expressing EhPNT-HA cultured with tunicamycin were subjected to immunoprecipitation with either anti-EhHgl or anti-HA antibody, followed by immunoblot analysis with either anti-EhHgl or anti-HA antibody, respectively. A filled arrowhead or an arrow indicates untreated or deglycosylated EhHgl, respectively. An open arrowhead indicates EhPNT.
