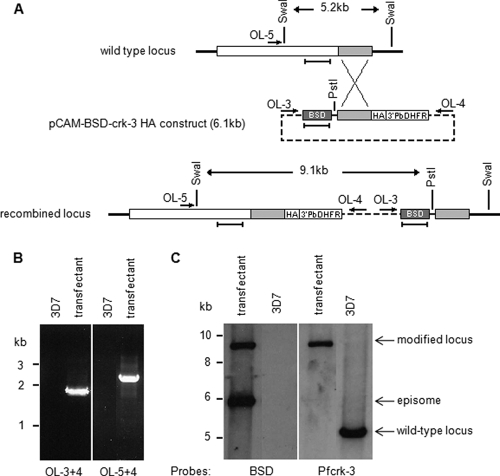
Fig. 5.
HA tagging of the pfcrk-3 locus. (A) Strategy for C-terminal tagging of pfcrk-3. The locations of PCR primers used for genotyping are indicated by arrows, restriction sites by vertical lines, and DNA probes by horizontal bars. See the text for details. (B) PCR analysis of HA-tagged locus. Total DNA isolated from blasticidin-resistant parasites transfected with pCAM-BSD-crk-3-HA and from wild-type 3D7 parasites was subjected to PCR using the primers indicated. (Left) Primers OL-3 and -4 (diagnostic for pCAM-BSD-crk-3 episome or concatemeric inserts); (right) primers OL-5 and -4 (diagnostic for 3′ integration). (C) Southern blot analysis. Total DNA was extracted from blasticidin-resistant parasites transformed with pCAM-BSD-crk-3 and from wild-type 3D7 parasites, and 3 μg was digested with PstI and SwaI, run on a 0.8% agarose gel, transferred to a Hybond membrane, and probed with the blasticidin resistance cassette (see panel A). The membrane was stripped and probed with a pfcrk-3 fragment that is not present in the pCAM-BSD-crk-3-HA plasmid (see panel A for the location of the probes, which are indicated by horizontal bars underneath the loci). The band corresponding to the linearized episome or concatemeric insert is detected in the transfected parasites (left panel, lower band). The band corresponding to the wild-type locus (right panel, right lane) is replaced by a larger band of the size expected from the recombination of the plasmid into the locus (both panels, left lanes).