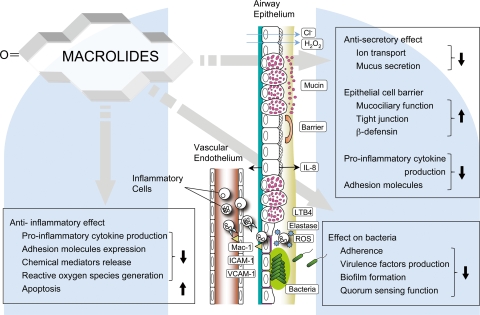
FIG. 2.
Beneficial effects of macrolides in the inflamed airway. In a chronically inflamed airway, there is epithelial cell damage, infiltration of inflammatory cells, goblet cell hyperplasia, hypersecretion, mucociliary dysfunction, and recurrent airway infection. Macrolides have been reported to attenuate inflammation and cellular damage in a variety of ways, as represented in this diagram. Downward-facing arrows, inhibition; upward-facing arrows, enhancement.