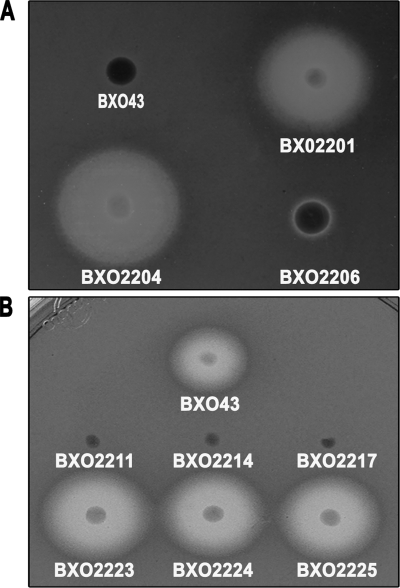
FIG. 3.
Siderophore production phenotype of X. oryzae pv. oryzae strains with mutations in genes involved in iron acquisition. Siderophore production is assayed as the presence of a halo around colonies growing on PSA-CAS medium. (A) An X. oryzae pv. oryzae feoB mutant overproduces siderophores. The X. oryzae pv. oryzae strains used are BXO43 (wild-type strain), BXO2201 (feoB1::pK18mob), BXO2204 (BXO2201/pHM1; vector control), and BXO2206 (BXO2201/pAP3; complemented strain). The pAP3 plasmid carries the cloned X. oryzae pv. oryzae feoB gene. (B) Mutations in xss genes result in a deficiency for siderophore production. Siderophore production was assessed by growth on PSA-CAS medium containing 100 μM DP. The X. oryzae pv. oryzae strains used are BXO43 (wild-type strain), BXO2211 (xssE1::pK18mob), BXO2214 (xssB1::pK18mob), BXO2217 (xssA1::pK18mob), BXO2223 (BXO2211/pAP15;, complemented strain), BXO2224 (BXO2214/pAP15; complemented strain), and BXO2225 (BXO2217/pAP15; complemented strain). The pAP15 cosmid contains the entire xss gene cluster of X. oryzae pv. oryzae. Plasmid pK18mob has an outreading lacZ promoter for transcribing downstream genes.