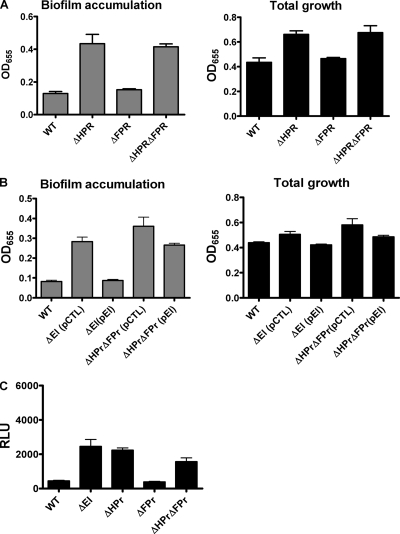
FIG. 4.
EI and HPr are in the same biofilm regulatory pathway. (A) Total growth and biofilm accumulation by wild-type V. cholerae (WT), a ΔHPr mutant, a ΔFPr mutant, and a ΔHPr ΔFPr double mutant. Biofilm accumulation by a ΔHPr mutant is significantly different from that by wild-type V. cholerae (P = 0.002), while biofilm accumulation by a ΔHPr ΔFPr is not significantly different from that by ΔHPr (P = 0.758). (B) Total growth and biofilm accumulation by wild-type V. cholerae (WT), as well as ΔEI and ΔHPr ΔFPr mutants rescued either with a control pBAD plasmid (pCTL) or a pBAD plasmid expressing a wild-type EI allele (pEI). Protein expression was induced by addition of 0.04% l-arabinose. Deletion of HPr and FPr blocked the ability of EI to repress biofilm formation. (C) Measurement of vps gene transcription in wild-type V. cholerae and various PTS mutants harboring a chromosomal vpsL-lacZ fusion. vpsL transcription in the ΔEI (P = 0.0002), ΔHPr (P < 0.0001), and ΔHPr ΔFPr (P = 0.0001) mutants is significantly different from that in wild-type V. cholerae. The error bars indicate standard deviations. RLU, relative light units.