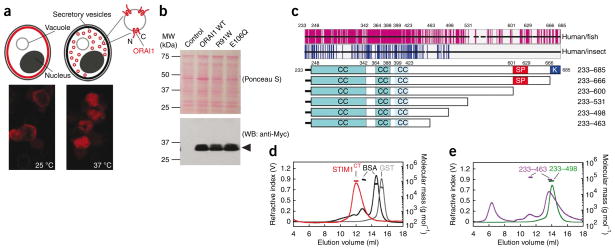
Figure 1.
Recombinant ORAI1 and STIM1 proteins used in the present study. (a) Above, ORAI1 (red shading) is incorporated into the plasma membrane of sec6-4 yeast at the permissive temperature, 25 °C, but accumulates in vesicles within the cell at the nonpermissive temperature, 37 °C. Cytoplasmic portions of ORAI1 in isolated vesicles face the external solution. Below, immunocytochemical localization of Myc-ORAI1 in sec6-4 cells grown at 25 °C and at 37 °C, respectively. (b) Western blot (WB) for Myc-ORAI1 in vesicles isolated from control yeast or from yeast expressing wild-type ORAI1, ORAI1R91W or ORAI1E106Q. (c) Above, sequence conservation in the STIM C-terminal region. Each horizontal black bar represents the human STIM1 sequence, with gaps introduced to maintain alignment with fish or insect orthologs. Vertical magenta lines indicate identity between human STIM1 and at least four of five fish orthologs; vertical blue lines indicate identity with at least two of three insect Stim proteins. Below, STIM1 cytoplasmic fragments with predicted coiled-coil (CC), Ser-Pro-rich (SP) and polybasic (K) regions indicated. (d) SEC-MALLS analysis of STIM1CT. Recombinant STIM1CT (red) migrated as a single symmetrical peak, with no evidence of aggregated protein in the void volume at ~5–8 ml. Plotted molecular mass estimates refer to the axis at right. STIM1CT experimental molecular weight (MW), 110.5 kDa; theoretical monomer MW, 54.7 kDa. Standards were BSA monomer and dimer (black) and glutathione S-transferase dimer (GST, gray). (e) SEC-MALLS profiles of STIM1233–498 (experimental MW, 70.1 kDa; theoretical monomer MW, 34.8 kDa) and STIM1233–463 (experimental MW, 87.5 and 119.6 kDa; theoretical monomer MW, 30.9 kDa). Standards (omitted from the plot for clarity) were the same as in d.