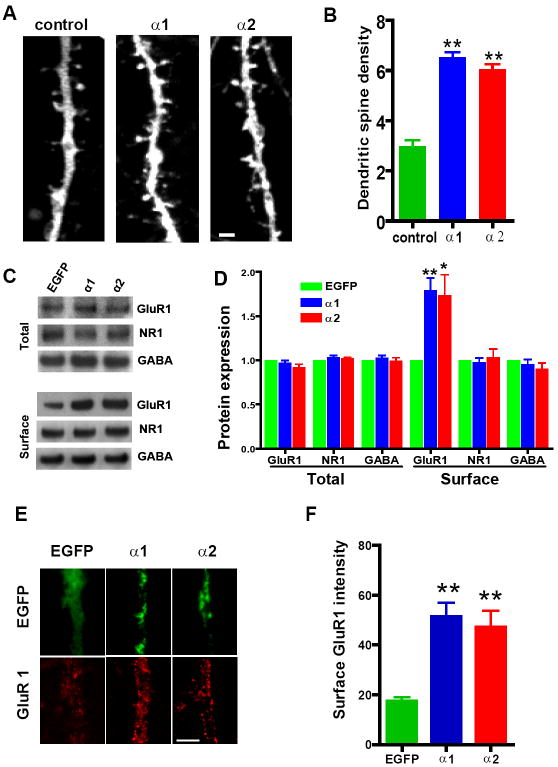
Figure 5. Forced Expression of α1- or α2-Takusan in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons Increases Dendritic-Spine Density and Surface GluR1 Labeling.
(A) Dendritic spines of cultured hippocampal neurons expressing mCherry alone (left), mCherry-α1 (center), or mCherry-α2 (right). Dendritic structures were visualized by EGFP expressed from a lentivirus. The size and number of dendritic spines increased in neurons expressing mCherry-α1 or -α2 compared to cells expressing mCherry alone. Scale bar = 5 μm. (B) Quantification of dendritic-spine densities in hippocampal cells expressing control mCherry alone (n = 7), mCherry-α1 (n = 7), or mCherry-α2 (n = 7). The density of dendritic spines (the number of spines per 10 μm) is significantly higher in cells expressing mCherry-α1- or mCherry–α2 than in control (**p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA). (C) Immunoblots of total and biotin-labeled (surface) proteins in hippocampal neurons infected with EGFP alone, EGFP-α1 or EGFP-α2. Proteins were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies against GluR1, NR1, or α1-subunit of GABAA. (D) Quantification of total or surface GluR1, NR1, or GABAA-α1 proteins. Intensities of immunoreactive bands were quantified relative to the control bands in 4 different experiments. Surface expression of GluR1, but not NR1 or GABAA receptor subunits, significantly increased after forced expression of EGFP-α1 or EGFP-α2 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA). (E) Immunocytochemistry of GluR1 surface labeling (red, bottom panel) on neurons expressing EGFP, EGFP-α1 or EGFP-α2. Scale bar = 5 μm. (F) Quantification of surface GluR1 labeling on dendrites. Mean intensity and SEM of GluR1 surface staining measured on dendritic membrane (n = 40 per sample). Forced expression of EGFP-α1 or -α2 led to an increase in GluR1 surface labeling (**p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA). Scale bar = 5 μm.