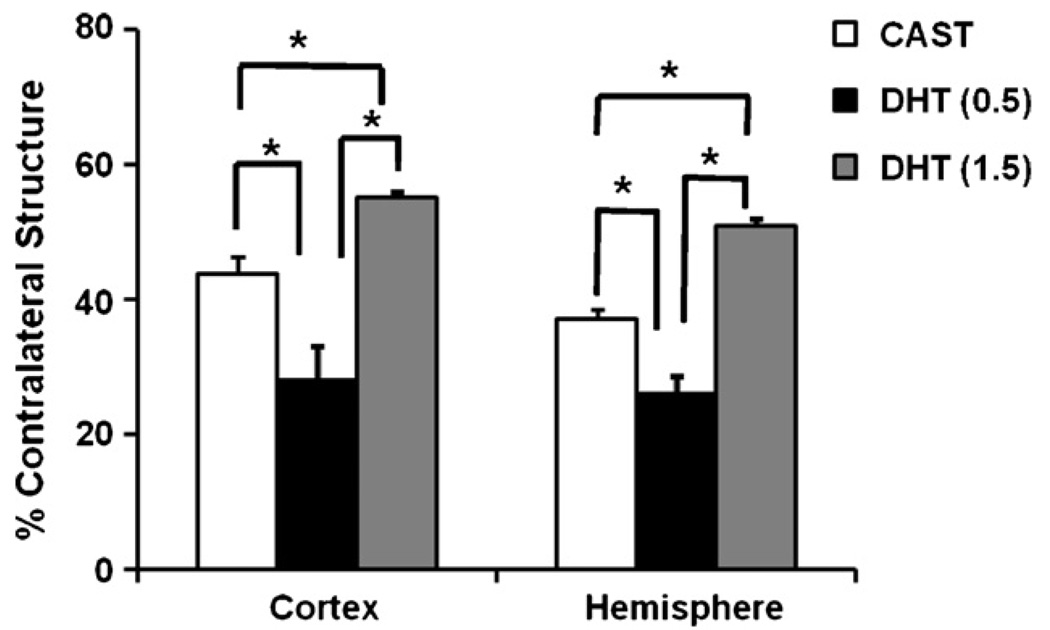
Fig. 1.
Dose-dependent effects of DHT in experimental stroke. Low physiological doses of DHT decrease, while high but physiologically relevant doses of DHT increase, infarct volumes in young adult castrated male mice following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Infarct volumes are expressed as percentages of contralateral structures in castrated mice (CAST, n = 20) and in castrates implanted with 0.5 mg DHT [DHT(0.5), n = 11] or 1.5 mg DHT [DHT(1.5), n = 12]. Values are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05. Adapted from data as published in Ref. [45].