Figure 2.
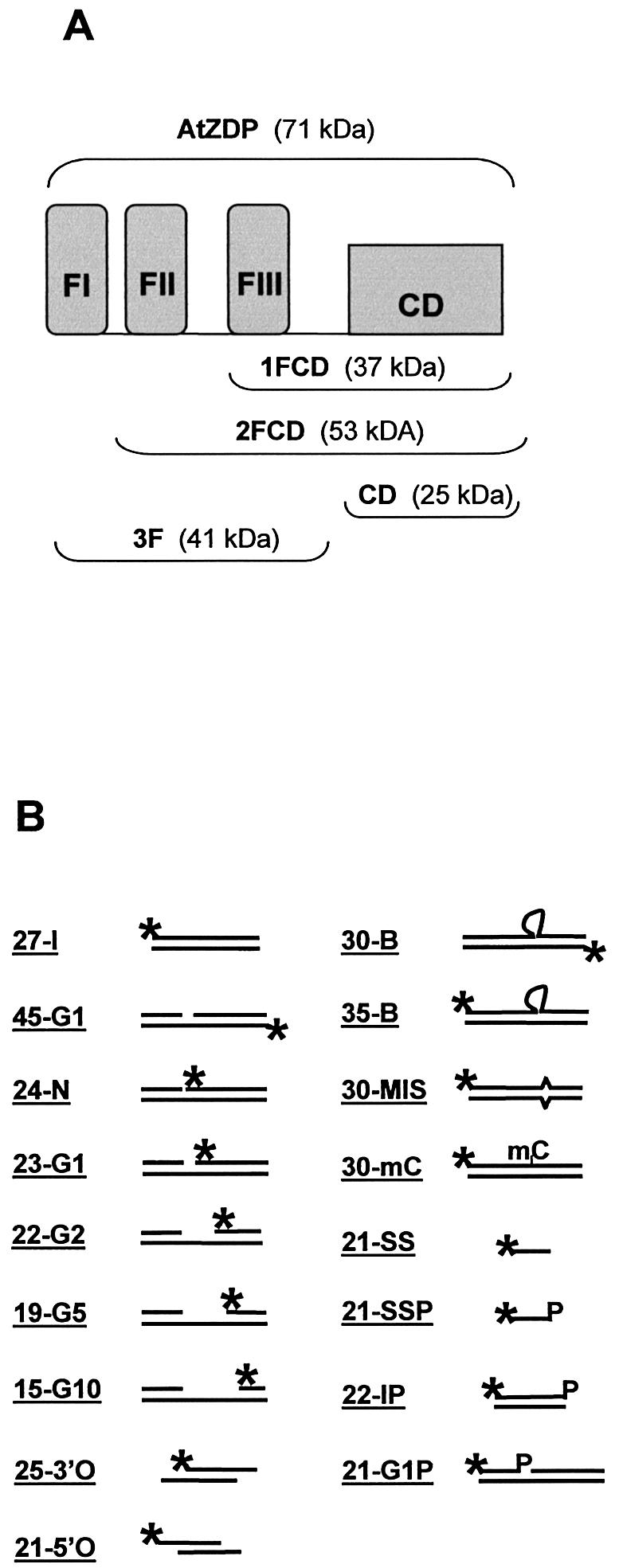
Structure of protein constructs and of oligo DNAs used in this work. (A) Schematic representation of the AtZDP deletion mutants. The three N-terminal PARP-like fingers (FI, FII, FIII, respectively) and the associated catalytic domain (CD) are shown as closed boxes. The modular composition of the wild type (above) and of the deletion mutants (below) are indicated with corresponding molecular weights enclosed in brackets. (B) Structure of the substrate oligonucleotides. The positions of 32P-labelled 5′-termini (asterisks) and of 3′-phosphate groups (P) are indicated. Heading numbers in oligo names refer to the length in bases of the labelled species. The 45-G1, 24-N, 23-G1, 22-G2, 19-G5, 21G1P are identical oligo- duplexes, only differing for the presence of a nick (24-N) or of a 1-base (45-G1, 23-G1, 21G1P), 2-base (22-G2), 5-base (19-G5), 10-base (15-G10) gap; the 25-3′O and the 21-5′O have overlapping double-strand domains with respectively 3′ or 5′ single-strand extensions on both strands; the 30-B, 35-B, 30-MIS, 30-mC only differ for the presence of a 5-nucleotide bulge (30-B and 35-B), a mismatched (30-MIS) or a methyl-cytosine (30-mC; see Materials and Methods for more details)
