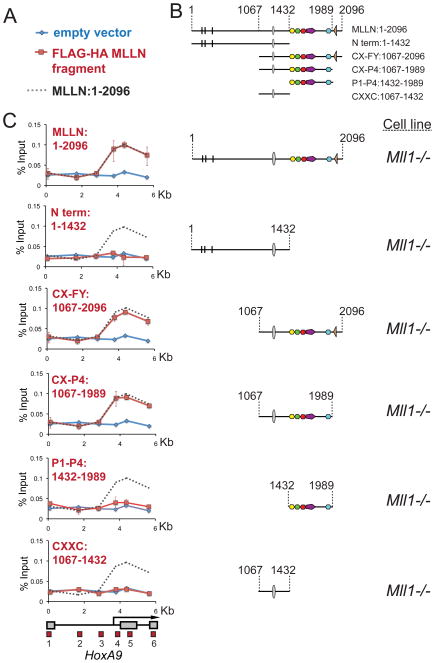
Figure 2. The CXXC domain and PHD fingers are sufficient for targeting MLL1 to the HoxA9 locus in vivo.
(A) Legend for the ChIP experiments in C. Blue line= ChIP in cells transfected with an empty vector, Red line= ChIP in cells transfected with the constructs indicated and Grey dots = the binding pattern of full length MLLN for comparison. (B) Schematics showing the series of deletion constructs. (C) The regions containing the MLL1 CXXC domain and the PHD fingers are both necessary for targeting MLL1 to the HoxA9 locus. Different fragments of the MLL1 N terminus were FLAG and HA (fh) double tagged and expressed in Mll1−/− MEFs and α-HA ChIP experiments were performed. ChIP results shown are typical for at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation of three separate PCR reactions. See also Figure S2.