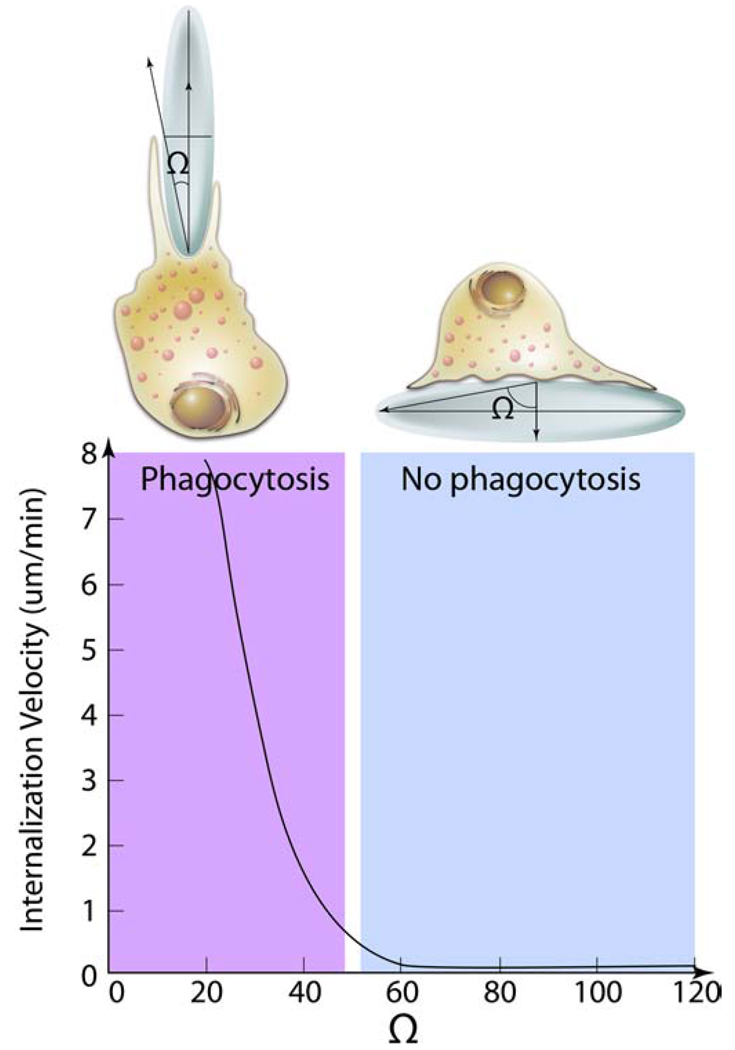
Fig. 4. Effect of particle geometry on phagocytosis.
The entry of a nanoparticles inside macrophages depends on the angle between the membrane normal at the point of initial contact and the line defining the particle curvature at this point (Ω). The internalization velocity is positive at Ω ≤ 45°, which indicates that the particle undergoes internalization. As the angle exceeds critical value ≈ (45°) the internalization velocity is zero, the macrophages lose the ability to entrap particles and start spreading over the particle.