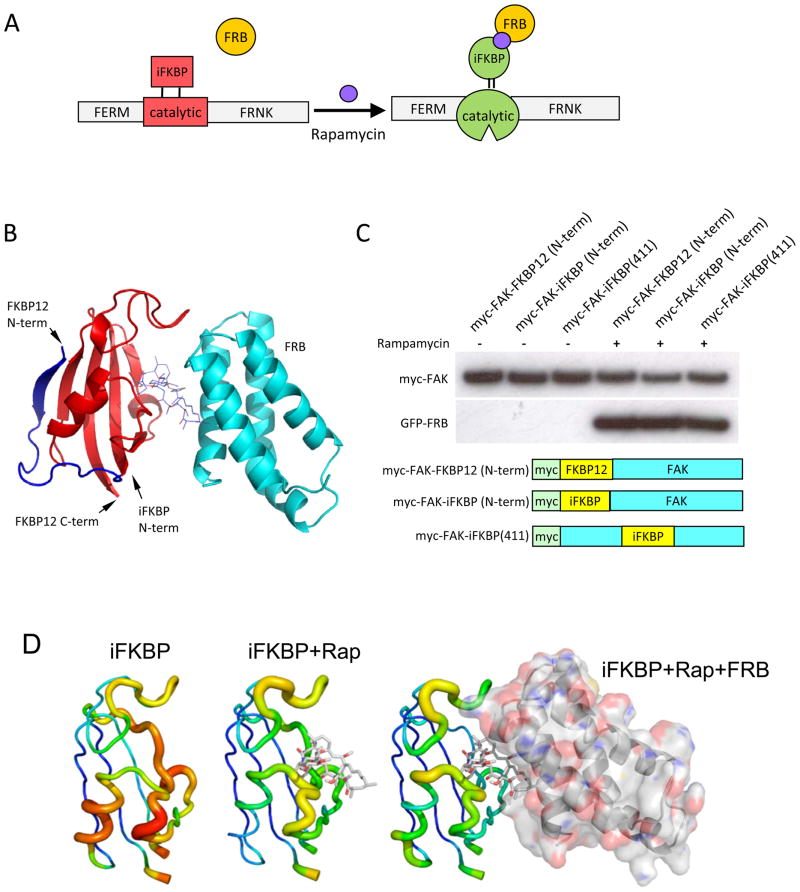
Fig. 1.
Design and generation of RapR-FAK. (A) Schematic representation of the approach used to regulate the catalytic activity of FAK. A fragment of FKBP is inserted at a position in the catalytic domain where it abrogates catalytic activity. Binding to rapamycin and FRB restores activity. (B) The truncated fragment of human FKBP12 (amino acids Thr22 through Glu108) inserted into the kinase domain. Blue and red, full length FKBP12; red, proposed structure of the inserted fragment. The FKBP12 is shown in complex with rapamycin and FRB (cyan). (C)Immunoblot analysis of iFKBP interaction with rapamycin and FRB. Myc-tagged FKBP12 and iFKBP constructs were immunoprecipitated from cells treated for 1 hour with either 200 nMrapamycin or ethanol (solvent control). Co-immunoprecipitation of co-expressed GFP-FRB was detected using anti-GFP antibody. (D) Changes in the molecular dynamics of iFKBP upon binding to rapamycin and FRB. Warmer colors and thicker backbone indicate increasing root mean square fluctuation (RMSF).