Figure 1. Expression of EGF components in insect ovaries.
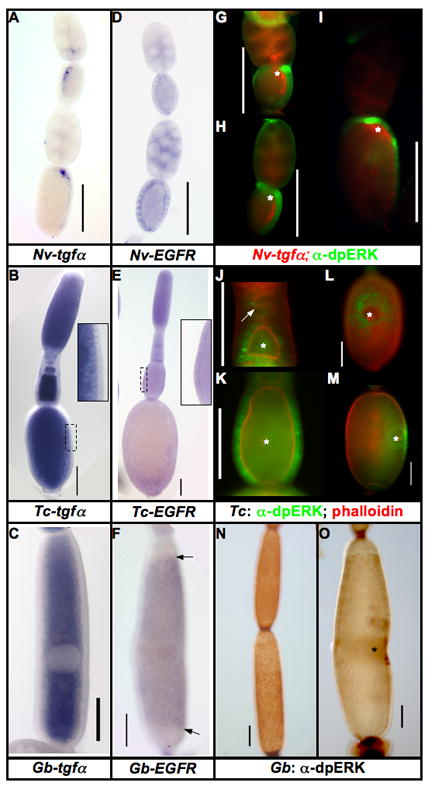
A–C: Expression of tgfα mRNA in the oocytes of N. vitripennis (A), T. castaneum (B), and G. bimaculatus (C). This mRNA is localized only in N. vitripennis, while it is ubiquitous in the oocytes of T. castaneum and G. bimaculatus.
D–F: Expression of EGFR mRNA in the follicular epithelium of N. vitripennis (D), T. castaneum (E), and G. bimaculatus (F) ovarioles. Arrows in F mark the borders of Gb-EGFR expression along the AP axis of the egg chamber.
G–I: Expression of Nv-tgfα mRNA (red) and dpERK (activated MAPK) (green) progressively older N. vitripennis ovarioles.
J–M: Expression of dpERK in T. castaneum ovarioles over the course of oogenesis (dpERK in green, phalloidin in red). dpERK expression is first detected in somatic cells lying just posterior to the very early oocytes (J, white arrow). In slightly older egg chambers, all follicle cells contacting the oocyte express dpERK (J, bottom egg chamber). As the follicle matures (K) dpERK remains strong in all lateral follicle cells, but is downregulated in the termini. During vitellogenesis (L (dorsal view), M (lateral view)), dpERK is found in the nuclei of the follicle cells surrounding the position of the oocyte nucleus, but not in the cells directly overlying it.
N–O: Expression of dpERK in G. bimaculatus ovarioles. G. bimaculatus shows a similar pattern to that of T. castaneum: in early egg chambers (N), dpERK is expressed in most of the follicle cells. In vitellogenic ovarioles, dpERK is markedly reduced in most of the follicular epithelium, except in the follicle cells in the vicinity of the oocyte nucleus (O). Scale bars represent 100μm, asterisks mark the position of the oocyte nucleus.
