Figure 3. EGF signaling is required for proper DV patterning in insects.
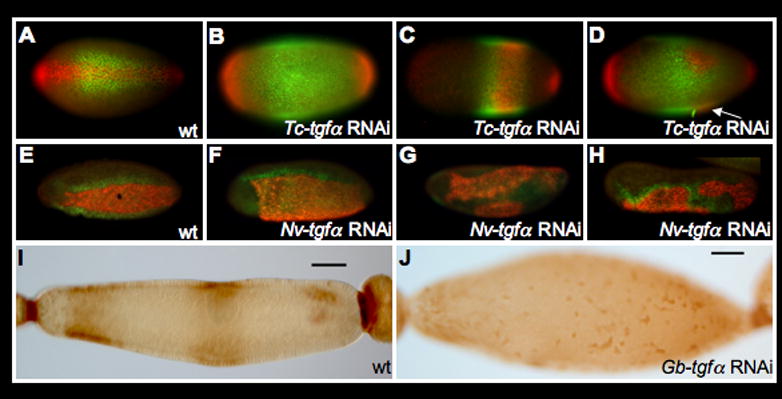
A–D: Disruption of DV polarity in T. castaneum after Tc-tgfα pRNAi as revealed by the expression of Tc-sog (green) and Tc-cact (red). A: Wild-type expression of Tc-sog and Tc-cact (ventral view). B–D: Representatives of different classes of Tc-tgfα pRNAi phenotypes (see text). Arrow in (D) indicates the out of focus additional ectopic spot of Tc-cact expression.
E–H: Disruption of DV polarity in N. vitripennis after Nv-tgfα pRNAi as revealed by the expression of Nv-twi (red) and Nv-vnd (green). E: Wild type expression pattern of Nv-twi and Nv-vnd (ventral-lateral view). F–H: Expression of Nv-twi and Nv-vnd in Nv-tgfα pRNAi embryos representing different phenotypic classes (see text for details).
I–J: After Gb-tgfα RNAi, the bilaterally symmetric banana shape, and strong activation of MAPK signaling (brown) over the oocyte nucleus of late egg chambers (I) are lost, giving rise to egg chambers with radial symmetry (J)
