Figure 1.
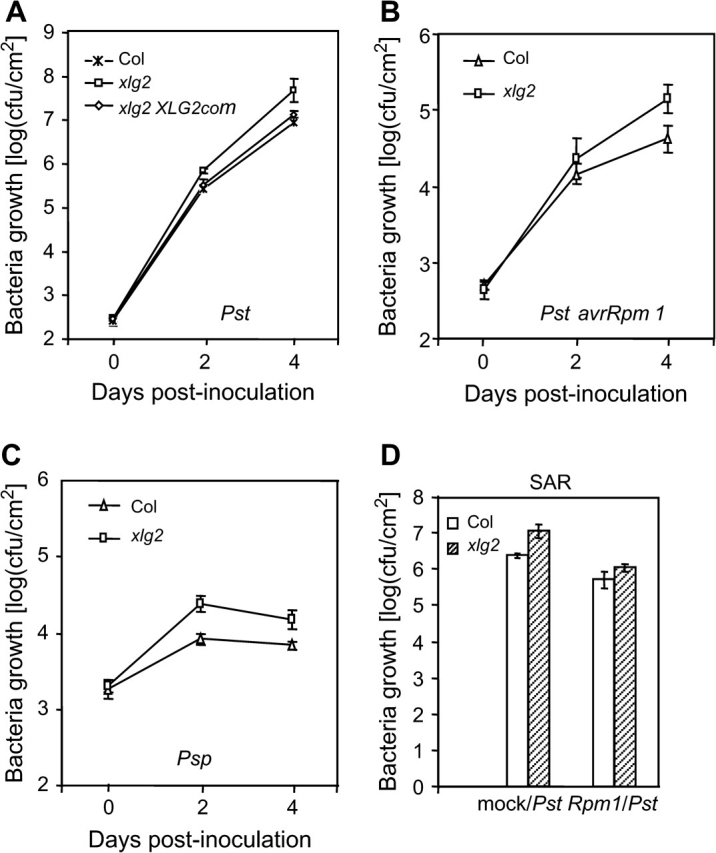
The xlg2 Mutation Leads to Enhanced Disease Susceptibility.
(A) The in-planta growth assays show a six-fold increase in bacterial growth in the mutant over the wt plants (Col). Leaves were hand-infiltrated with the virulent Pst strain and bacterial numbers in the infected leaves were counted 2 and 4 d post inoculation. The mutant's enhanced disease susceptibility phenotype was complemented by the XLG2 transgene (XLG2com) expressed in the xlg2 mutant.
(B, C) The xlg2 mutation also compromises resistance to the avirulent Pst avrRpm1 strain (B) and to the non-host strain Psp (C).
(D) The xlg2 mutant is not defective in induction of SAR. Induction of SAR by Pst avrRpm1 led to an over five-fold decrease in growth of Pst in both the mutant and wt plants. Rpm1/Pst: four to five leaves of each plant were inoculated with Pst avrRpm1 to induce SAR and, 3 d later, other upper leaves were infected with virulent Pst. Mock/Pst: no SAR induction prior to infection with Pst; plants had been mock-inoculated with water before infection with Pst. Shown are the bacterial colony forming units (cfus) in the leaves 4 d post infection with Pst. Each data point represents the average of three replicates ± standard deviation.
