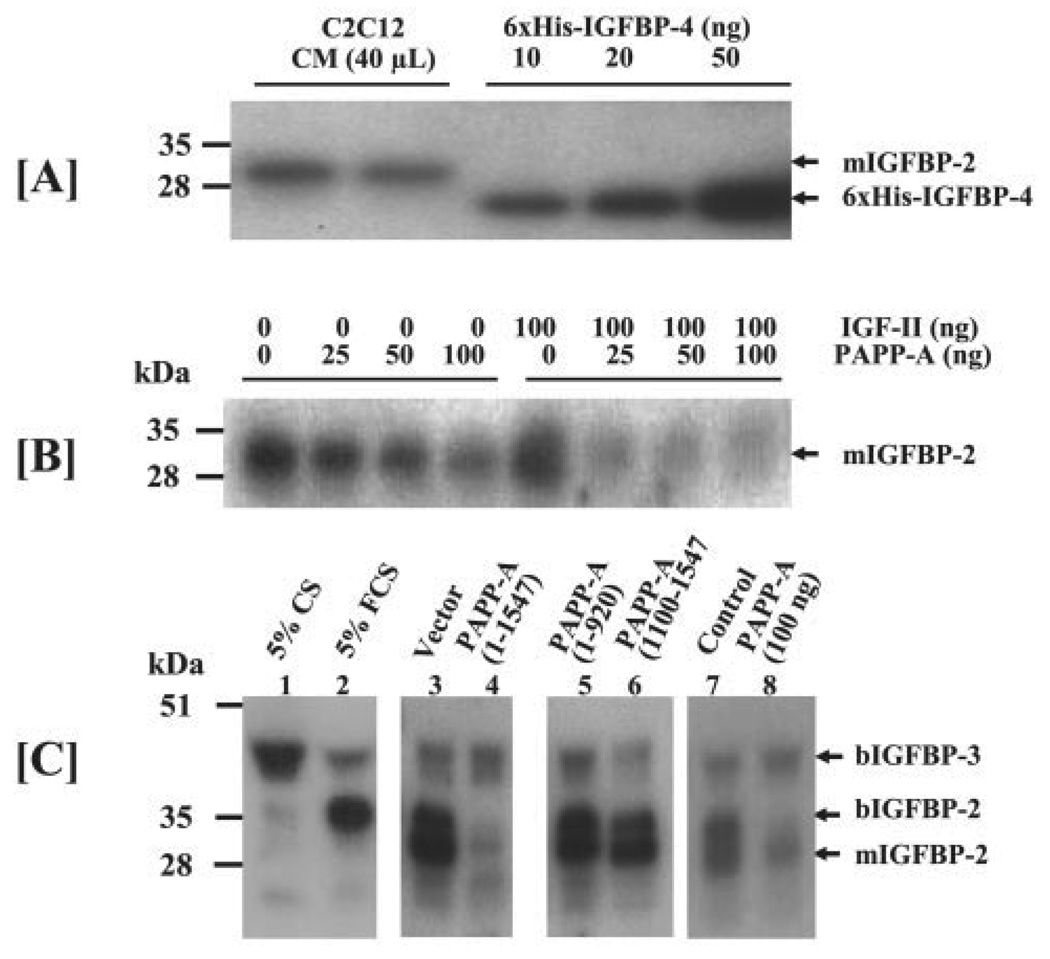
FIGURE 6. [125I]IGF-II ligand blot analysis of the IGFBPs in C2C12 cultures.
A, C2C12 myoblasts were seeded in 10-cm dishes in DMEM containing 10% fetal calf serum. Upon 100% confluence, cells were rinsed twice with DMEM and cultured in DMEM/0.1% bovine serum albumin for an additional 48 h prior to collection of CM. 40 µl of CM was subjected to [125I]IGF-II ligand blot analysis. Recombinant His6-IGFBP-4 was used as a standard to estimate the amount of total IGF binding activity in the CM samples. The 30-kDa IGFBP, previously identified as the murine IGFBP-2 (mIGFBP-2), is the primary IGFBP produced by C2C12 myoblasts. B, 40 µl of serum-free C2C12CM was incubated for 20 h at 37 °C with increasing concentrations of recombinant PAPP-A in the absence or presence of 100 ng of IGF-II. Incubated CM was then subjected to [125I]IGF-II ligand blot analysis. The data presented here show that PAPP-A cleaves the mIGFBP-2 in a dose-dependent manner and the cleavage of mIGFBP-2 is further increased in the presence of IGF-II. C, 40 µl of CM from either C2C12 myoblasts that were treated with 100 ng/ml PAPP-A (pooled from three independent experiments) or transfected with PAPP-A expression plasmid (pooled from two independent experiments) were subjected to IGF-II ligand blot analysis in order to measure proteolysis of IGFBPs. 5% CS or 5% FCS was used to differentiate the exogenous IGFBPs from the endogenous IGFBPs in the CM. The data show degradation of the 30-kDa mIGFBP-2 and 34-kDa bovine IGFBP-2 (bIGFBP-2) in the CM of the C2C12 cultures treated with exogenous PAPP-A or those transfected with PAPP-A-(1–1547). The levels of mIGFBP-2 or bIGFBP-2 in the CM of C2C12 myoblasts transfected with either PAPP-A-(1–920) or PAPP-A-(1100–1547) were not affected.