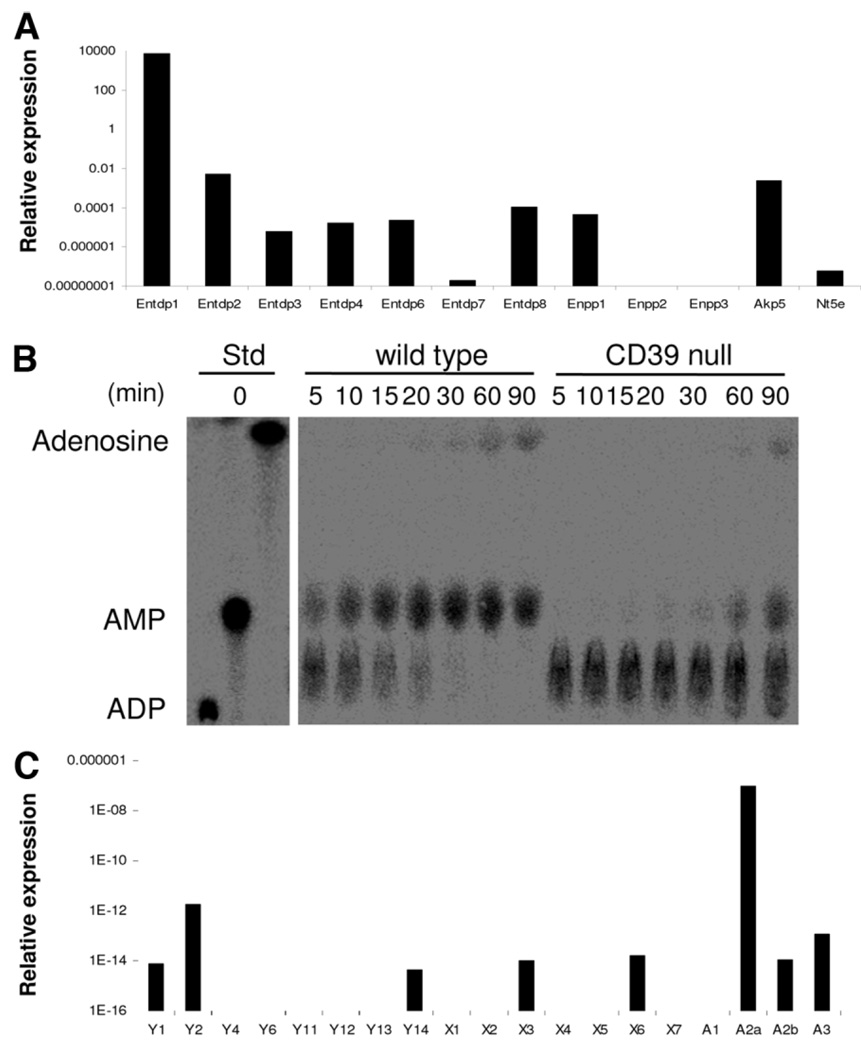
Fig. 1.
Expression patterns of ectonucleotidases and purinergic receptors on NK cells. Isolated splenic NK (NK1.1-positive, CD49b-positive, CD3-negative) cells from Rag1−/− mice were studied by reverse transcription PCR. (A) Among all the ectonucleotidases tested, the highest expression was noted for CD39/E-NTPDase1. Expression levels of other ectonucleotidases, nucleotide pyrophosphatase (Enpp), and alkaline phosphatase (Akp5) were significantly lower and ecto-5′-ectonucleotidase/CD73 (Nt5e) was near absent. (B) Analysis of NTPDase activity on NK cells was done by TLC. The products of [14C]ADP hydrolysis by purified hepatic NK cells are shown. Extracellular nucle-otides were efficiently hydrolyzed to AMP and adenosine by wild-type cells, whereas cells null for CD39 show substantially delayed hydrolysis of nucleotides and limited production of aden-osine. (C) Isolated NK cells expressed the P2 receptors P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y14, P2X3, and P2X6; NK also expressed the P1 receptors A2A (at high levels), as well as A2B and A3 but not A1.