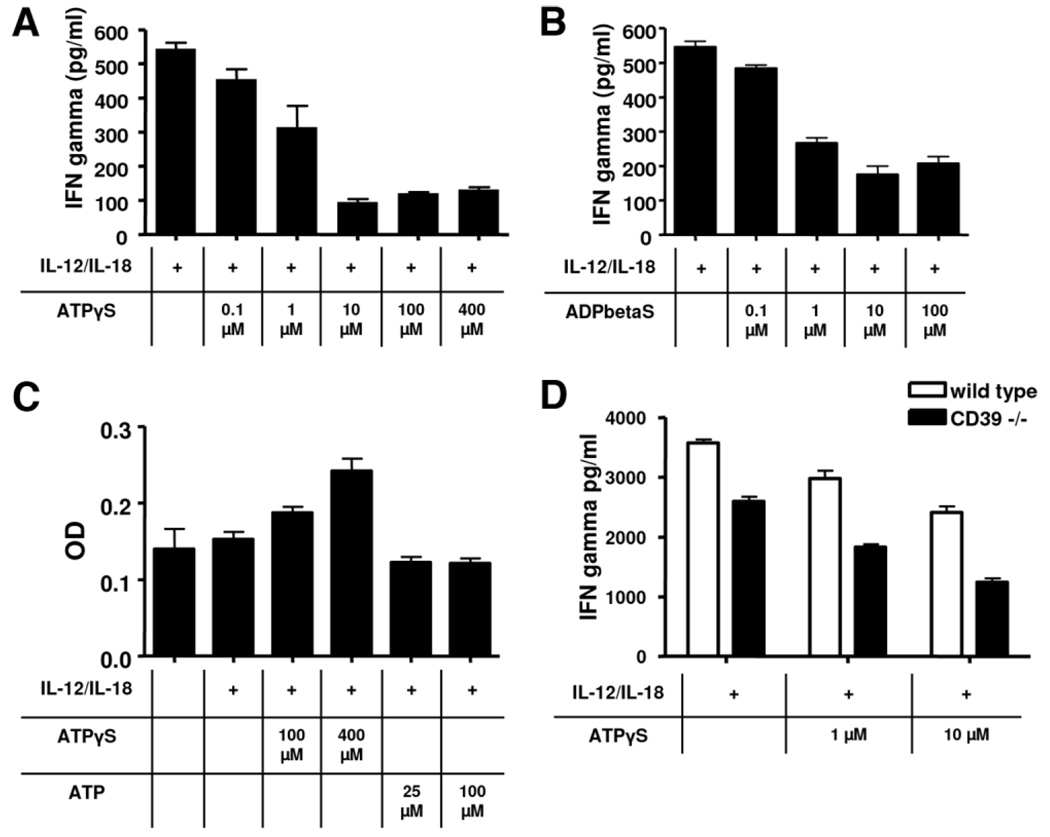
Fig. 6.
Secrrtion of INFγ by NK cells in vitro. Splenic NK cells were isolated from mice null for CD39 and matched the wild-types. Secretion of IFNγ was induced by administration of IL-12 and IL-18 for 24 hours. (A,B) Addition of ATPγS or ADPβS (nonhydrolyzable ATP/ADP analogs) significantly decreased secretion of IFNγ in a dose-dependent manner. (C) Analysis of cell viability after 36 hours of incubation using a MTT assay: Administration of ATPγS resulted in a dose-dependent increase of optical density. (D) Comparison of IFNγ secretion of wildtype versus CD39-null NK cells. Deletion of CD39 is associated with significantly reduced secretion of IFNγ. Graphs are representative of at least five experiments. Data are given as mean ± standard deviation.