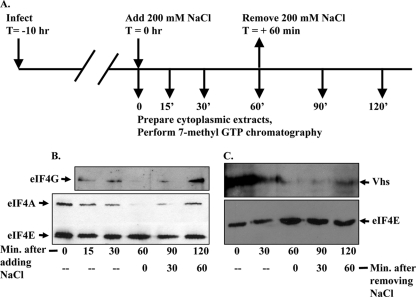
FIG. 3.
Hypertonic shock causes rapid and reversible disruption of eIF4F and reversible dissociation of Vhs from the material that binds 7-methyl GTP-Sepharose 4B. (A) Timeline of the experiment. Ten hours after infection with 10 PFU/cell of wild-type HSV-1 (strain KOS), HeLa cells were subjected to hypertonic shock by replacing the medium with medium that had been supplemented with 200 mM NaCl in addition to that which is present in normal medium. Cells were harvested and lysed, and cytoplasmic extracts were prepared at the time of initiation of the shock or at various subsequent times. For some cultures, the medium was removed 60 min after initiation of the shock and replaced with normal isotonic medium. Cytoplasmic extracts were prepared at various times after reversal of the shock. Binding assays were performed to analyze proteins that bound 7-methyl GTP-Sepharose 4B. (B) Bound proteins were eluted from the beads by boiling in SDS sample buffer and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting to detect eIF4E, eIF4G, and eIF4A. (C) Aliquots from the same samples analyzed in panel B were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting to detect eIF4E and Vhs.