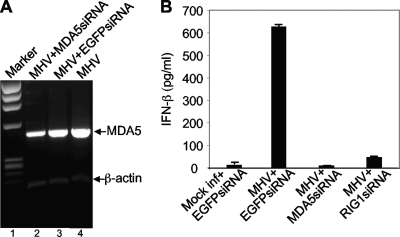
FIG. 8.
Role of MDA5 in MHV-induced IFN-β signaling. (A) Knockdown of MDA5 mRNA by siRNA. N20.1 cells were transfected with siRNAs specific to MDA5 or EGFP or mock transfected. At 24 h posttransfection, cells were infected with MHV-A59/GFP at an MOI of 10. At 24 h p.i., cellular mRNAs were isolated and amplified by RT-PCR with primers specific to mouse MDA5 or β-actin (see Materials and Methods). The molecular weight marker is indicated on the left (lane 1), and the bands representing MDA5 and β-actin are indicated with arrows. (B) Effect of MDA5 knockdown on IFN-β induction. The experiment was identical to that described for panel A but with additional controls that include mock infection and transfection with EGFP siRNA as a negative control for the inability to induce IFN-β and MHV infection and transfection with RIG-I siRNA as a positive control for the inhibition of IFN-β induction. The amount of IFN-β protein was quantified with the ELISA kit and expressed as the mean picograms per ml for three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations of the means.