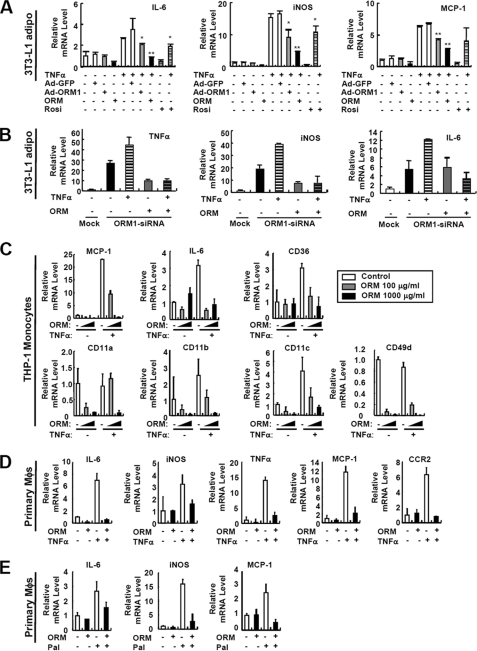
FIGURE 5.
ORM suppresses inflammatory gene expression in adipocytes, monocytes, and macrophages. A, effect of ORM treatment and adenoviral overexpression of Orm1 in TNFα-induced inflammatory gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Adenovirus-infected (50 multiplicities of infection, 2 days postinfection) or noninfected adipocytes were incubated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of ORM (250 μg/ml). Dose of ORM treatment was determined according to the circulating ORM level in normal mice. mRNA levels of inflammatory genes were analyzed by Q-PCR analysis. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. n = 2 or 3. iNOS, inducible nitric-oxide synthase; Rosi, rosiglitazone; IL-6, interleukin 6. B, knockdown of Orm1 induces inflammatory gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. 3T3-L1 stable cell lines overexpressing mock or mouse Orm1-specific siRNA were established by retroviral infection and following selection with puromycin. At day 7 of adipocyte differentiation, the cells were treated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) and/or ORM (250 μg/ml) for 24 h. mRNA levels of inflammatory genes were measured by Q-PCR analysis. C, ORM suppresses the expression of certain genes involved in inflammation and cell adhesion in THP-1 monocytes. THP-1 monocytes were incubated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of ORM (100 or 1000 μg/ml) for 6 h. mRNA levels of inflammatory genes were analyzed by Q-PCR analysis. D, ORM (250 μg/ml) suppresses TNFα-induced inflammatory gene expression in mouse peritoneal macrophages (Mϕs). E, ORM (250 μg/ml) suppresses palmitate (Pal)-induced inflammatory gene expression in mouse peritoneal macrophages.