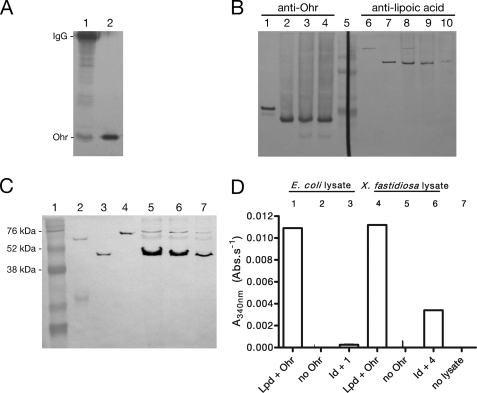
FIGURE 1.
In vivo interaction of Ohr with lipoylated proteins. A, Ohr co-immunoprecipitated with lipoylated enzymes. Proteins were precipitated with anti-lipoic acid and were analyzed by Western blot with anti-Ohr. Lane 1, immunoprecipitated proteins on beads (30 μl); lane 2, recombinant Ohr (0.1 μg). The His tag from recombinant Ohr (lane 2) was previously digested by thrombin treatment. B, fractions containing extracellular proteins were obtained by washing cells twice with Tris buffer. Lanes 1–4, anti-Ohr (1:1000); lanes 6–10, anti-lipoic acid (1:5000). Lane 1, recombinant Ohr (0.1 μg); lane 2, X. fastidiosa lysate; lane 3, supernatant first wash; lane 4, supernatant second wash; lane 5, RainbowTM markers; lane 6, recombinant LpdA (0.1 μg); lane 7, recombinant SucB (0.1 μg); lane 8, X. fastidiosa lysate; lane 9, supernatant first wash; lane 10, supernatant second wash. All recombinant proteins possess a His tag. C, immunodetection of lipoate enzymes in X. fastidiosa lysates. Lane 1, RainbowTM markers; lane 2, PDHB (0.1 μg); lane 3, SucB (0.1 μg); lane 4, LpdA (0.1 μg); lanes 5–7, X. fastidiosa lysates (15, 10, and 5 μg, respectively). D, ability of immunodepleted (Id) E. coli (Ec) and X. fastidiosa (Xf) lysates to support Ohr peroxidase activity. Bacterial lysates (0.5 mg/ml) were incubated with NADH (0.2 mm), Ohr (1 μm), Lpd (2.5 μm), and t-BHP (0.2 mm). For more details on the experimental procedures employed here, see the supplemental material.