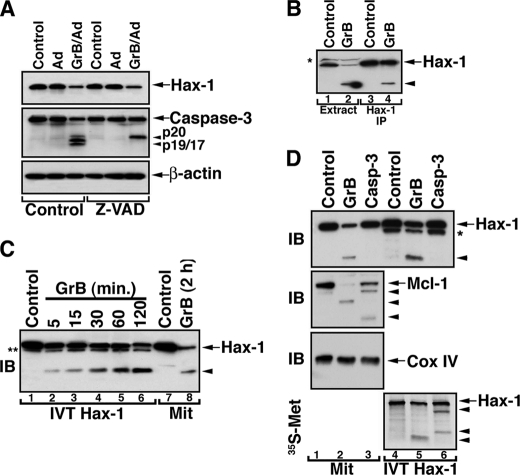
FIGURE 3.
Direct and preferential cleavage of Hax-1 by GrB. A, loss of Hax-1 expression in GrB/Ad-treated cells is not attenuated in the presence of the caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-fluoromethyl ketone. Jurkat cells were treated with GrB/Ad (33 nm/10 pfu/ml) in the presence or absence of the pancaspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-fluoromethyl ketone (100 μm). The cells were lysed in the presence of GrB inhibitor, as described above, and assessed by immunoblotting for the expression of Hax-1, caspase-3, and β-actin. B, direct GrB cleavage of immunoprecipitated Hax-1. GrB (66 nm) was applied to the extract of Jurkat cells (lane 2) or a pellet of the protein A·anti-Hax-1·Hax-1 complex immunoprecipitated from the Jurkat cell extract (lane 4). Controls were the untreated extract or the Hax-1 immunoprecipitant (lane 1 and 3, respectively). Reaction products were resolved by SDS-PAGE and assessed by immunoblotting with anti-Hax-1 Ab. GrB acts directly on endogenous Hax-1 because immunoprecipitated (IP) Hax-1 is cleaved by GrB. C, direct GrB activity on in vitro translated Hax-1. In vitro translated Hax-1 was co-incubated with GrB (66 nm) for the indicated time periods (lanes 1–6). Lysates of control or GrB-treated mitochondria (lanes 7 and 8) were run on SDS-PAGE side by side with the in vitro translated Hax-1 to compare migration patterns. The asterisk indicates an unidentified protein band. D, mitochondrial Hax-1 is preferentially cleaved by GrB, although in vitro translated Hax-1 is also a caspase-3 substrate. Mitochondria purified from Jurkat cells (lanes 1–3) or 35S-labeled in vitro translated Hax-1 (lanes 4–6) were left untreated or treated with GrB (66 nm) or recombinant caspase-3 (100 nm). The reaction products were assessed by immunoblotting (IB) for the presence of the indicated proteins and by autoradiography for the 35S-labeled fragment(s) of in vitro translated Hax-1. Mitochondrial Hax-1 was cleaved by GrB but not by recombinant caspase-3 (top), and the GrB cleavage product had a migration pattern similar to that of GrB-treated in vitro translated (IVT) Hax-1 (lanes 2 and 5). The activity of GrB and caspase-3 was confirmed by their activity on mitochondrial Mcl-1 (second panel). Cox IV serves to demonstrate equal loading of mitochondrial proteins (third panel). Autoradiographic assessment of IVT Hax-1 cleavage products suggests that it is cleaved by either GrB or caspase-3, although different cleavage fragments are produced. The arrowheads indicate cleavage products. The asterisk indicates an unidentified protein band present in the in vitro translation mixture.