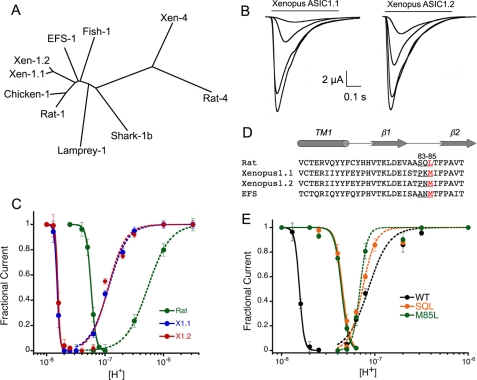
FIGURE 1.
Properties of Xenopus xASIC1.1 and xASIC1.2 and effect of mutations in the β1-β2 linker in proton affinity. A, cladogram generated by Clustal alignment of ASIC proteins. Xen, Xenopus. B, whole-cell currents of xASIC1.1 and xASIC1.2 evoked by sequential application of solutions of pH 7.3, 7.1, 6.8, and 6.5. Between stimuli, the external solution was returned to pH 8.0 for 30 s. C, dose response curves to protons of xASIC1.1 (X.1), xASIC1.2 (X.2), and rat ASIC1a (Rat). D, amino acid sequence alignment of transmembrane domain 1 and the β1-β2 linker of rat, Xenopus, and EFS ASIC1. E, dose response curves to protons of xASIC1.1 (WT) with a pH50D of 7.8, n = 10, pH50A of 7.0 (n = 3.2), and the mutant xASIC1-P83S-K84Q-M85L (SQL) with a pH50D of 7.35 (n = 9.4) and a pH50A of 7.1 (n = 3.7). Symbols represent the mean of 8–10 independent cells ± S.D. Lines are the fit of the data to Equation 1. Error bars are ± standard deviation (S.D.).