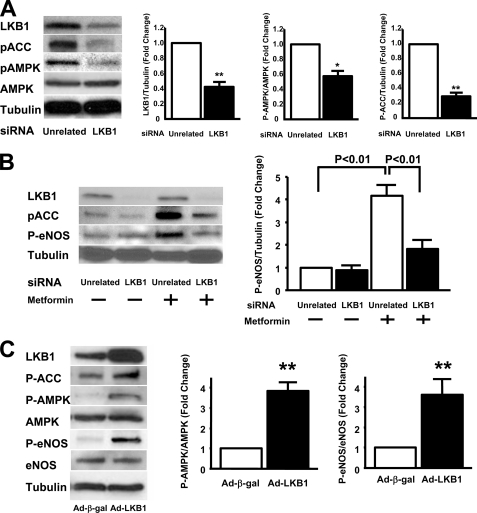
FIGURE 4.
Transduction with siRNA targeting LKB1 diminished an AMPK signaling in HUVECs. A, LKB1 is required for full AMPK signaling. Western blot analysis for LKB1, phosphorylated ACC at Ser-79 (pACC), phosphorylated AMPK at Thr-172 (pAMPK), total AMPK (AMPK), and α-tubulin (Tubulin) is shown. Right panel shows quantification of LKB1, pAMPK, and pACC. *, p < 0.05 versus unrelated siRNA (n = 3 in each group). HUVECs were treated with siRNA targeting LKB1 for 48 h. B, LKB1 is required for metformin-stimulated eNOS phosphorylation. Western blot analysis for LKB1, phosphorylated ACC, phosphorylated eNOS (P-eNOS), and α-tubulin is shown. HUVECs were treated with siRNA targeting LKB1 for 48 h followed by treatment with metformin (2 mm) or vehicle for 3 h. A representative Western immunoblot is shown. C, LKB1 overexpression activates AMPK signaling and leads to an increase in eNOS phosphorylation. Western blot analysis for LKB1, phosphorylated-ACC at Ser-79, phosphorylated-AMPK at Thr-172, total AMPK, phosphorylated-eNOS at Ser-1177, total eNOS, and α-tubulin is shown. HUVECs were infected with Ad-β-gal or Ad-LKB1 for 24 h. Right panels show quantitative Western blot analyses for P-AMPK and P-eNOS. **, p < 0.01 versus Ad-β-gal treatment (n = 3 in each group).