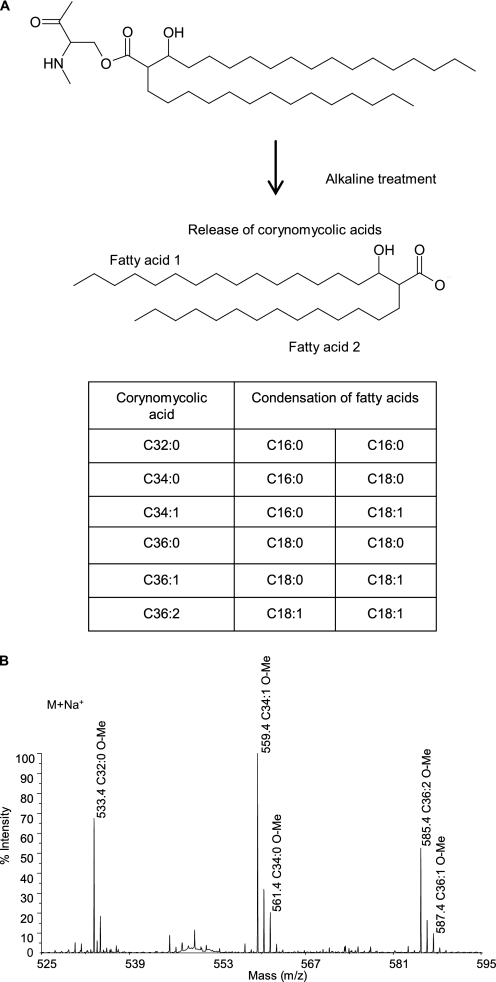
FIGURE 2.
Analysis of corynomycolic acids resulting from the alkaline treatment of the hydrophobic protein extract of C. glutamicum. A, structures of the corynomycoloyl residue that substitutes the serine 15 in CgPorA and of the resulting putative free corynomycolic acids upon alkaline treatment of the hydrophobic polypeptides. These fatty acids are produced through an enzymatic condensation between two regular sized (saturated or monounsaturated) fatty acids (C16 or C18). B, reflectron MALDI-TOF mass spectrum of the corynomycolic acid methyl esters obtained by alkaline treatment, followed by methylation, of the hydrophobic proteins. The observed peaks correspond to those of pseudomolecular ions (M+Na+).