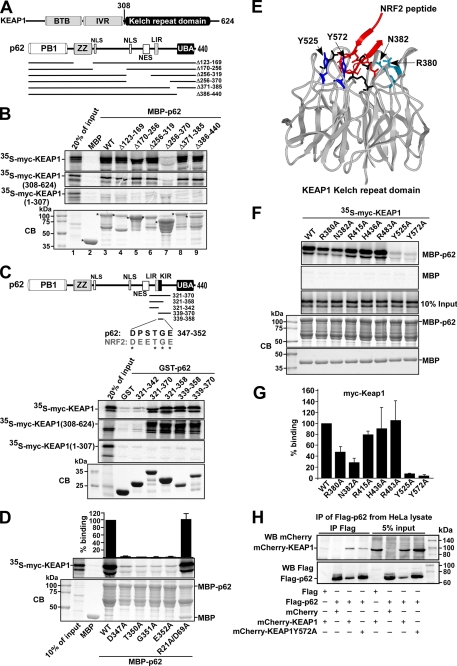
FIGURE 3.
The p62 protein interacts with KEAP1 via a short, conserved sequence motif. A, maps of KEAP1 and p62 indicating positions of domains and the deletion constructs employed in B to map the interaction between the two proteins. B, MBP pulldown assays showing that amino acids 321–370 in p62 are essential for binding to KEAP1, and that p62 interacts with the Kelch-repeat domain of KEAP1. The KEAP1 constructs that are depicted were in vitro translated in the presence of [35S]methionine, and tested in MBP pulldown assays for interaction with the indicated MBP-p62 constructs. The bottom gel panel shows a Coomassie Blue (CB)-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel with the various MBP-p62 constructs used as input in the pulldown assays. Full-length proteins are indicated with asterisks. C, GST pulldown assays showing that amino acids 339–358 of p62 are sufficient for the interaction with KEAP1. The GST-p62 constructs, which contained the indicated peptides from p62, were tested in GST pulldown assays for interaction with the indicated Myc-tagged portions of KEAP1 produced by in vitro translation; full-length KEAP1 (1–624 amino acids), a C-terminal Kelch-repeat-containing fragment (308–624 amino acids), and an N-terminal BTB domain- and IVR-containing fragment (1–307 amino acids) were tested. The figure at the top shows the p62 constructs used and an alignment between p62 and NRF2 of the conserved DXXTGE motif (amino acids 347–352 in p62). D, MBP pulldown assays showing the effect of single point mutations in the DXXTGE motif of p62. Quantifications of the mean % binding with standard deviations from three independent experiments are shown above the autoradiograph. E, schematic based on the crystal structure of the Neh2 peptide from NRF2 bound to the Kelch-repeat domain of KEAP1. Seven amino acid residues located in loops of the Kelch-repeat were selected for mutational analyses to determine their effect on binding to p62. F and G, mapping of amino acid residues in the Kelch-repeat domain important for interaction with p62. The indicated single-point mutation constructs of KEAP1 were tested in MBP pulldown assays with MBP-p62. Quantification of the mean % binding with standard deviations from three independent experiments are shown. H, mCherry-KEAP1 co-immunoprecipitated with FLAG-p62 from HeLa cell extracts. Cells were co-transfected with the indicated constructs and FLAG-p62 immunoprecipitated with FLAG antibodies 24 h after transfection. Precipitated FLAG-p62 and co-precipitated mCherry-KEAP1 were detected by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. For B, C, and H, data representative of three independent experiments with similar results are shown.