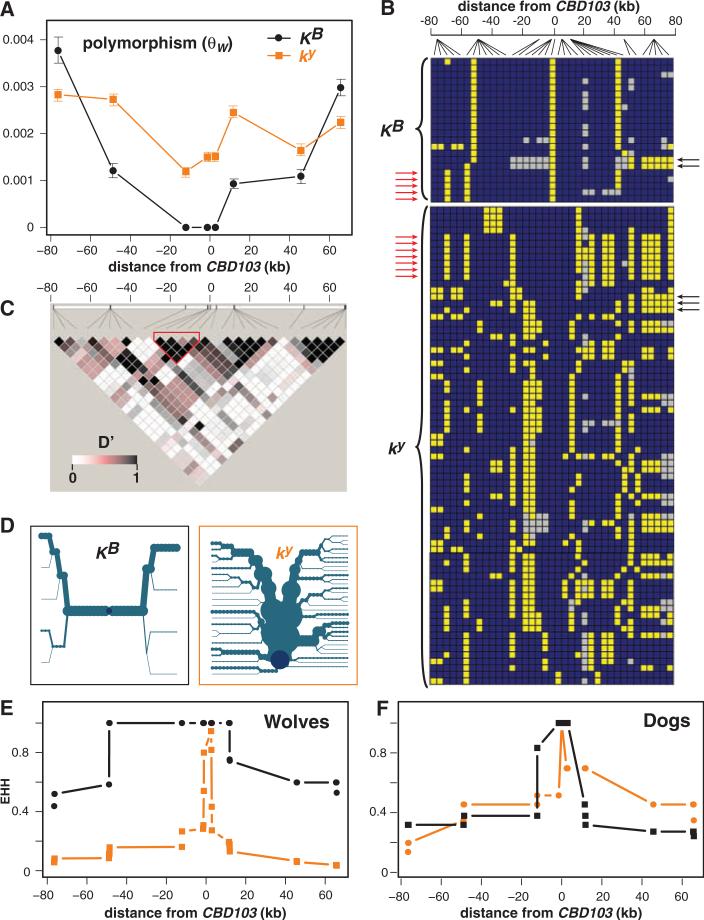
Fig. 2.
Polymorphism and haplotype structure of the K locus in North American gray wolves [(A) to (E), 1 KB/KB, 20 KB/ky, and 26 ky/ky] and domestic dogs [(F), 6 KB/KB and 6 ky/ky]. (A) Polymorphism (θW, ±SD) as a function of distance from CBD103. (B) Wolf haplotype structure was inferred on the basis of 36 SNPs; each row represents a KB- or ky- bearing chromosome; blue and yellow squares represent the major and minor alleles, respectively; and the gray squares represent missing data. Red and black arrows indicate examples of haplotypes likely to represent historical recombination between KB- and ky-bearing chromosomes at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the locus, respectively. (C) Pairwise LD values (expressed as D') for all wolf chromosomes; the red outline indicates a core region (as in Fig. 3) unlikely to have undergone historical recombination. (D) Haplotype bifurcation diagrams for KB- or ky-bearing chromosomes, in which the central dark blue dot represents CBD103, branches represent haplotype divergence, and the thickness of the lines is proportional to the number of chromosomes. (E and F) EHH for KB- or ky-bearing chromosomes in wolves (E) and dogs (F) as a function of distance from CBD103ΔG23.