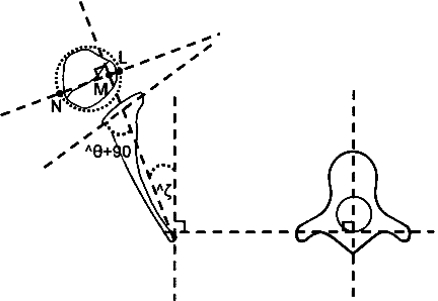
Fig. 5.
Schematic drawing showing the method of calculating glenoscapular angle (glenoid version θ) and posterior subluxation of the humeral head. The scapular line that connects the medial aspect of the scapula and the mid-glenoid is drawn. A second line is drawn connecting the posterior and anterior margins of the glenoid. 90° is subtracted from the angle of the posterior medial quadrant defined by these lines to determine the glenoid version θ. A line perpendicular to the scapular line is drawn and the percentage of posterior subluxation is defined as the ratio of the distance from the scapular line to the anterior portion of the head to the diameter of the humeral head (LM/LN × 100)