Fig. 2.
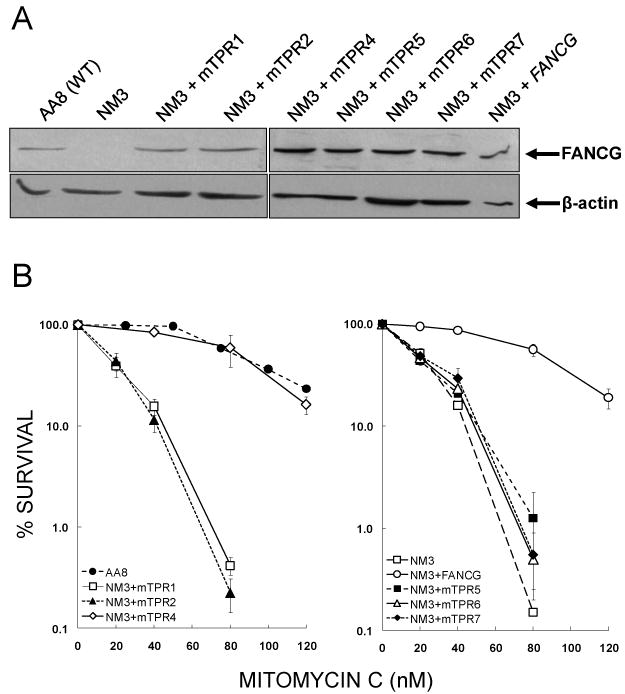
Validation of NM3 cell lines used to study FANCG and FANCG-mediated protein interactions. (A) Expression of mutated human FANCG protein in NM3 cell lines. Western blotting was used to determine expression of FANCG protein in NM3 cell lines transfected with human cDNA mutated at the indicated TPR motif. Clones that expressed FANCG at similar levels to each other and at a similar level to the endogenous expression of wild type hamster protein (AA8) were selected for further study. β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) MMC survival responses of NM3 cell lines expressing human FANCG with mutated TPR motifs. Clonogenic survival assays were performed with curves shown representing the means of 2-4 experiments and error bars showing the standard error of the mean (SEM). The responses of NM3 cell lines with mutated TPR1, TPR2, TPR5, TPR6 and TPR7 (respective D37 values = 22, 25, 29, 29 and 32 nM MMC) were similar to NM3 (D37 = 26 nM MMC), whilst the response of NM3+mTPR4 (D37 = 101 nM MMC) was similar to the wild type cell line AA8 (D37 = 99 nM MMC) and NM3 complemented with wild type human FANCG cDNA (D37 = 100 nM MMC).
