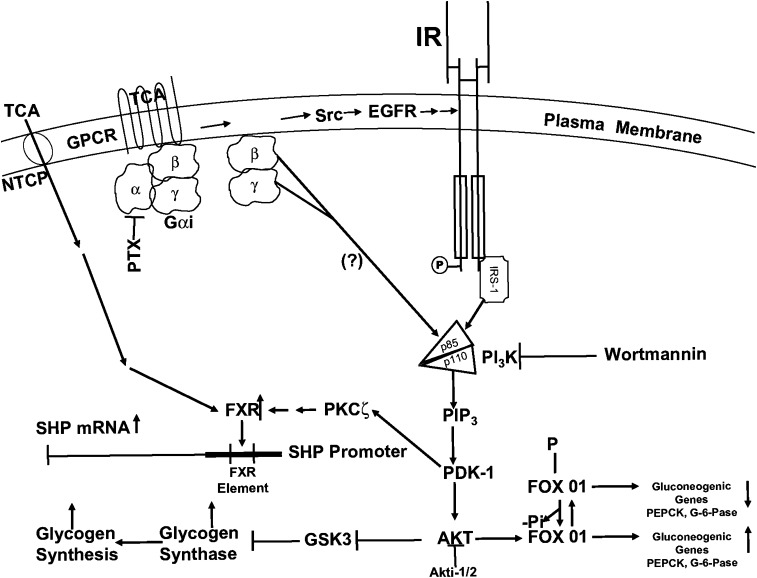
Fig. 11.
Cell signaling model for the regulation of glucose metabolism in hepatocytes by taurocholate. TCA can rapidly activate Gαi-dependent G-protein coupled receptor(s) that activate the AKT (insulin signaling pathway). Activated AKT is known to downregulate gluconeogenic genes by phosphorylation of FOX01 and to activate glycogen synthase by phosphorylation of GSK3. PDK-1 in the insulin signaling pathway activates PKCζ, which increases the ability of TCA to activate the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and increases the transcription of the gene encoding SHP. The induction of SHP protein may play a role in the long term (>3 h) repression of gluconeogenic genes. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptor; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase-3; IR, insulin receptor; NTCP, Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; PDK-1, phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1; PI3K, phosphoinositide-3-kinase; PTX, pertussis toxin; Src, Src kinase; SHP, small heterodimeric partner; TCA, taurocholate.