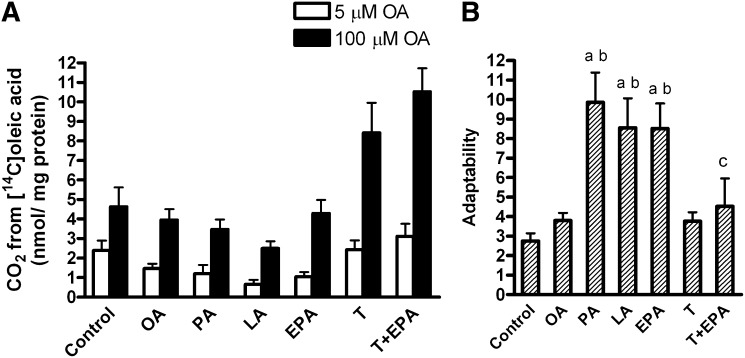
Fig. 5.
Adaptability. Myotubes were pretreated for 24 h with 1 µM T0901317 or vehicle (DMSO), and then for another 24 h with 100 µM OA, EPA, LA, PA, 40 µM BSA (control), T0901317 plus BSA, or a combination of T0901317 and EPA, and thereafter underwent CO2 trapping for 4 h with 5 or 100 µM [14C]OA in the absence of glucose as described in “Materials and Methods.” (A) Oxidation of 5 and 100 µM OA. Fatty acid oxidation increased by 64% upon increased availability of OA (overall effect P < 0.001). (B) Adaptability was defined as the ability to increase the acute OA oxidation with increasing OA concentration and calculated as follows: [oxidation of 100 µM OA / oxidation of 5 µM OA]. Results represent means ± SEM for n = 6–12. Bonferroni correction was applied for multiple comparisons. aP < 0.05 versus control; bP < 0.05 versus OA; cP < 0.05 versus EPA. EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; LA, linoleic acid; OA, oleic acid; PA, palmitic acid; T, T0901317.