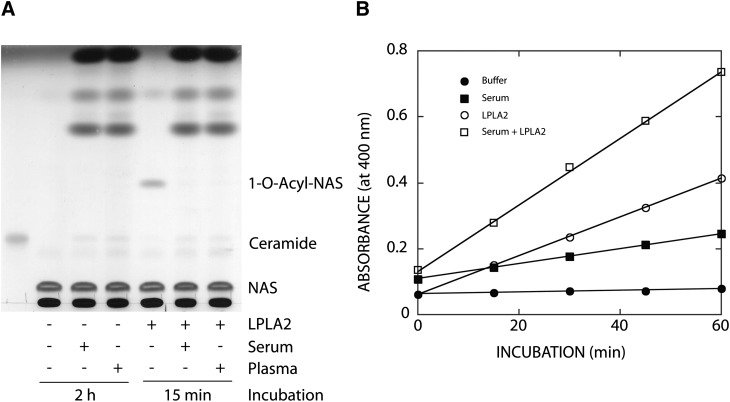
Fig. 1.
Effect of plasma or serum on LPLA2 activity. A: Transacylase activity of LPLA2. The reaction mixture contained 48 mM sodium citrate (pH 4.5), 10 µg/ml BSA, liposomes (130 µM phospholipid), 1.3% human serum, 1.3% human plasma, or 14.5 ng/ml of recombinant mouse LPLA2 in the presence or absence of 1.3% human serum or 1.3% human plasma in 500 µl of total volume. Liposomes consisting of DOPC/sulfatide/NAS (3:0.3:1, molar ratio) were incubated with the enzyme for 2 h or 15 min at 37°C as shown in A. The reaction products were extracted and separated by an HPTLC plate using a solvent system consisting of chloroform/acetic acid (9:1, v/v). The reaction product, 1-O-acyl-NAS, is produced by LPLA2. B: Esterase activity of LPLA2. The reaction mixture contained 200 µM p-nitro-phenylbutyrate, 48 mM sodium citrate (pH 4.5), 10 µg/ml BSA, and 14.5 ng/ml of recombinant mouse LPLA2 in the presence or absence of 1.3% serum in 500 µl of total volume. The reaction was initiated by adding the recombinant LPLA2 and kept for 10, 20, 30, and 40 min at 37°C. One hundred microliters of the reaction mixture was taken at each time point and mixed with 100 µl of cold 0.2 M NaHCO3. The absorbance of the mixture at 400 nm was measured immediately.