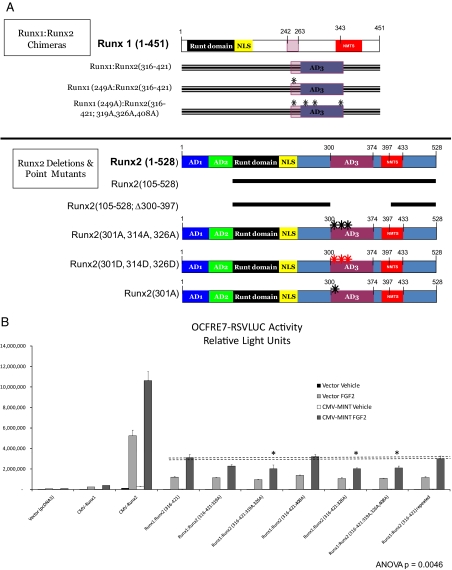
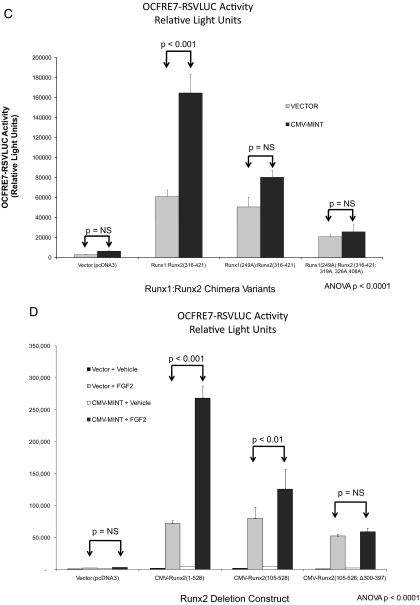
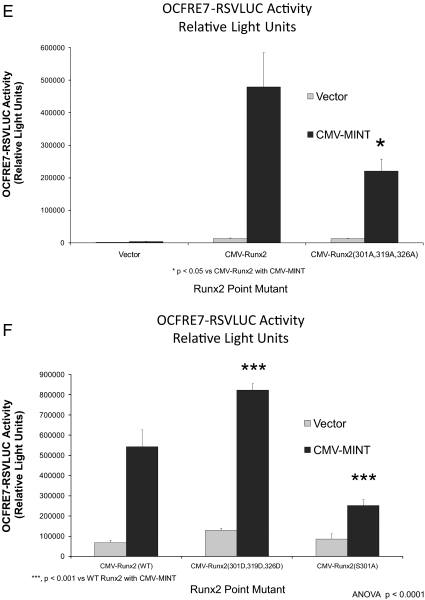
Figure 4.
Activation of Runx2 AD3 by MINT+FGF2 requires intact proline-directed kinase cognates. The OCFRE reporter OCFRE7-RSVLUC was used as a reporter to assess a systematic series of CMV-Runx1:Runx2 chimeras and CMV-Runx2 point mutants in transient transfection assays. A, Schematic representation of Runx1:Runx2 chimeras (upper panel) and Runx2 deletion and point mutants (lower panel) analyzed. Black asterisks, S/T → A point mutations that disrupt potential Pro-directed phospho-acceptor sites. Red asterisks, S/T → D point mutations that introduce phosphomimetic changes at potential Pro-directed phospho-acceptor sites. B, AL mutagenesis of the Runx1:Runx2(316-421) chimera revealed contribution of Thr326 in AD3. *, P < 0.05 vs. nonmutated chimera control treated with MINT+FGF2. C, Additional Ala mutagenesis of Runx1 Ser249, equivalent to Runx2 Ser301, in Runx1:Runx2(316-421) chimera abrogated MINT+FGF2 activation. D, Deletion of Runx2 residues 300–397 in the context of Runx2 abrogated MINT+FGF2 induction. E, Point mutations that destroy Pro-directed phosphor-acceptor sites at residues Ser-301, Ser-319, and Thr-326 in native full-length Runx2 significantly reduce MINT-dependent trans-activation without affecting basal activity. F, Conversely, the Runx2(301D, 319D, and 326D) phosphomimetic mutations increase activation by MINT. Mutation of Ser-301 to Ala in context of full-length Runx2 reduces basal activity as observed in Runx1:Runx2 chimeras. NS, Not significant.