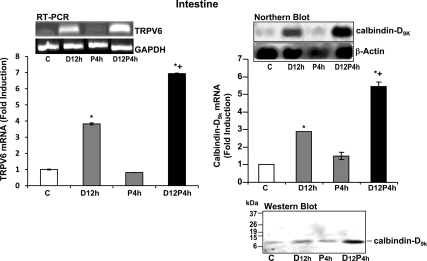
Figure 2.
Prolactin (P) has cooperative effects with 1,25(OH)2D3 (D) in regulating duodenal calcium transport genes. RT-PCR analysis of TRPV6 mRNA expression (left panel) or Northern blot analysis of calbindin-D9k mRNA (right panel) in the duodenum of vitamin D-deficient male mice injected with either vehicle (C, control), 1,25(OH)2D3 (2 ng/g bw D12 h), or prolactin (1 μg/g bw P4 h) at 12 or 4 h before termination, respectively, or 1,25(OH)2D3 + prolactin (D12, P4 h) at 12 and 4 h before termination, respectively. Bottom right, Western blot analysis of calbindin-D9k protein. Bars represent the mean ± sem, n = 4–6/group. *, P < 0.05 compared with control; +, P < 0.05 compared with D12 h. P4 h vs. C. P > 0.5; a single injection of prolactin and termination at 2, 6, or 12 h after prolactin injection also did not result in a significant effect on TRPV6 mRNA or calbindin-D9k mRNA (data not shown).