Figure 2.
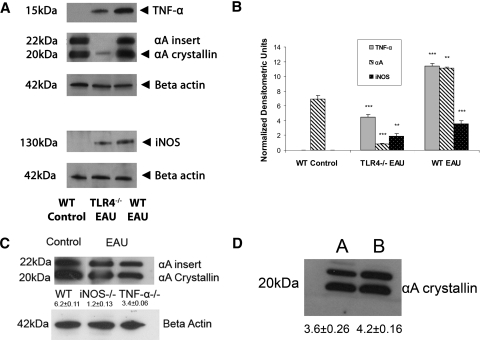
During early EAU, TNF-α, αA crystallin, and iNOS were significantly upregulated compared with both nonimmunized WT control and TLR4−/− mice with EAU (A, B). There was no upregulation of αA crystallin in iNOS−/− or in TNF-α−/− mice in early EAU (C). There was no significant increase in the expression of αA crystallin in the mice treated with CFA and pertussis toxin (D; A, WT control; B, WT injected with pertussis toxin). Equal amounts of total retinal proteins from day 7 WT control, WT EAU, TLR4−/−, TNF-α−/−, and iNOS−/− mice with EAU and WT mice injected with CFA and pertussis toxin were separated on a 15% SDS-polyacrylamide gel (7.5% gel for iNOS). Protein bands were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with monoclonal TNF-α, polyclonal anti–αA-crystallin, and polyclonal anti-iNOS as the primary antibodies and with corresponding secondary antibodies tagged with horseradish peroxidase. TNF-α was detected at the molecular mass indicated (∼15 kDa), αA crystallin was detected at ∼20 kDa protein, and iNOS was detected at ∼130 kDa protein. Equal protein loading was confirmed by reprobing blots with monoclonal antibody to β-actin. There was a significant decrease in αA crystallin in the day 7 EAU retina of TLR4−/− mice compared with the WT control retina. (B) Densitometry measurements show a threefold decrease in TNF-α, a 13-fold decrease in αA crystallin, and a twofold decrease in iNOS protein in TLR4−/− mice with early EAU compared with WT EAU mice. There was also a ninefold decrease in αA crystallin in TLR4−/− mice with early EAU compared with WT control. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001; ***P < 0.0001.